Spinalis origin and insertion
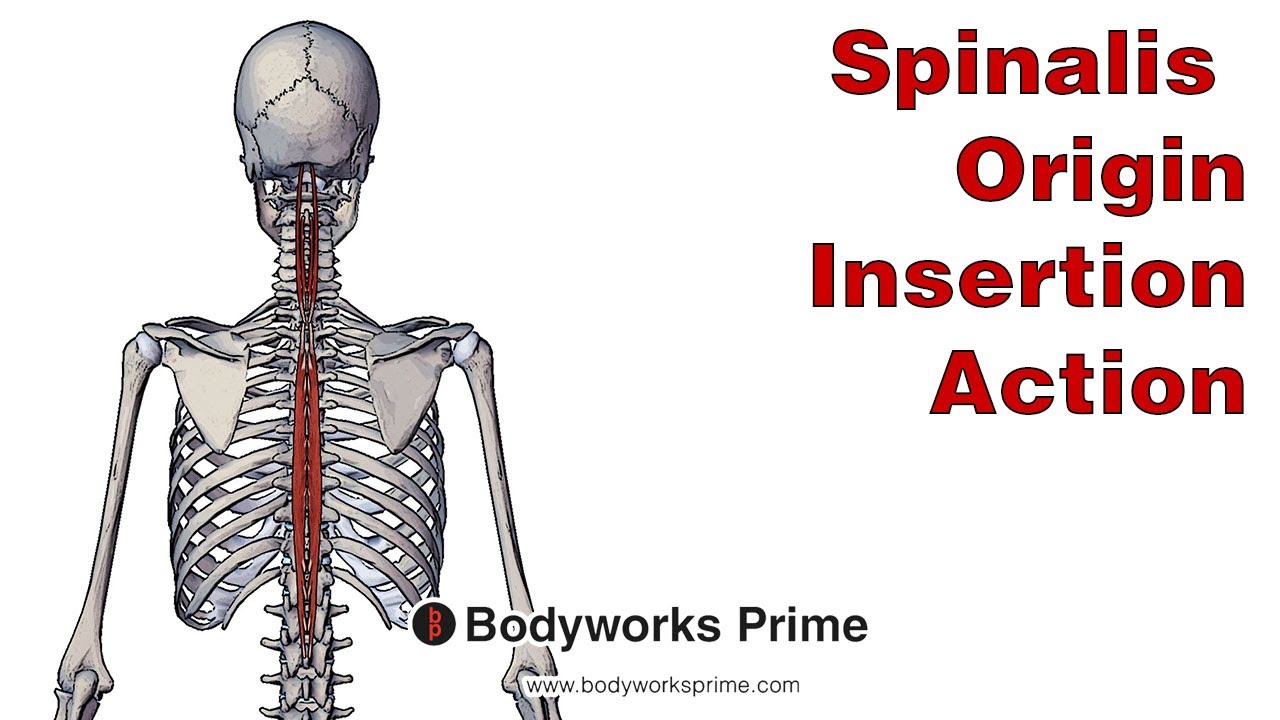
The spinalis muscle is situated in the middle and upper back as well as the neck, running parallel to the spine. It plays an important spinalis origin and insertion in extending the back and neck, while also aiding in lateral flexion movements. The spinalis muscle is a member of the erector spinae muscle group.
The spinalis muscle is the most medial of the erector spinae group of muscles, and is lateral to the multifidus group. The spinalis detaches from medial side of the longissimus thoracis and travels forward near thoracic vertebral spinous processes to cervical vertebral spinous processes. It may be divided into two parts:. In the pig and the horse, the spinalis muscle forms a common muscle belly, therefore sometimes termed as "spinalis thoracic et cervicis thoracic and cervical spinal muscle ", whereas in ruminants and carnivores, the thoracic and cervical spinalis muscles receive additional muscular strands from the the mamillary and transverse processes of some vertebrae, and the fibers of the spinlais musccles are closely related to and often difficult to separate form the semispinalis muscle. Therefore, some authors use the compound name "thoracic and cervical spinal and semispinal muscle" to describe this muscular complex.
Spinalis origin and insertion
The spinalis is a deep muscle of the back. It is the smallest of the muscle columns within the erector spinae complex, and can be divided into the three parts — thoracic, cervicis and capitis although the cervicis part is absent in some individuals. It is the smallest of the muscle columns within the erector spinae complex, and can be divided into the three parts - thoracic, cervicis and capitis although the cervicis part is absent in some individuals. Once you've finished editing, click 'Submit for Review', and your changes will be reviewed by our team before publishing on the site. We use cookies to improve your experience on our site and to show you relevant advertising. To find out more, read our privacy policy. Spinalis Home Encyclopaedia S Spinalis. Not yet rated. Attachments: Arises from the lower thoracic and lumbar vertebrae, sacrum, posterior aspect of the iliac crest, and the sacroiliac and supraspinous ligament. It attaches to the spinous processes of C2, T1-T8 and the occipital bone of the skull. Actions: Acts unilaterally to laterally flex the vertebral column. Acts bilaterally to extend the vertebral column and Innervation: Posterior rami of the spinal nerves. Blood Supply: Muscular branches of vertebral artery, deep cervical artery, and posterior branch of posterior intercostal artery By TeachMeSeries Ltd Click to Load.
Bilateral contraction results in neck extension, while unilateral contraction causes ipsilateral lateral flexion of the neck [10].
The spinalis is a portion of the erector spinae , a bundle of muscles and tendons , located nearest to the spine. It is divided into three parts: Spinalis dorsi, spinalis cervicis, and spinalis capitis. Spinalis dorsi, the medial continuation of the sacrospinalis , is scarcely separable as a distinct muscle. It is situated at the medial side of the longissimus dorsi , and is intimately blended with it; it arises by three or four tendons from the spinous processes of the first two lumbar and the last two thoracic vertebrae : these, uniting, form a small muscle which is inserted by separate tendons into the spinous processes of the upper thoracic vertebrae, the number varying from four to eight. It is intimately united with the semispinalis dorsi , situated beneath it. Spinalis cervicis, or spinalis colli, is an inconstant muscle, which arises from the lower part of the nuchal ligament , the spinous process of the seventh cervical, and sometimes from the spinous processes of the first and second thoracic vertebrae , and is inserted into the spinous process of the axis , and occasionally into the spinous processes of the two cervical vertebrae below it.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. The muscles of the back categorize into three groups.
Spinalis origin and insertion
The spinalis Latin: musculus spinalis is one of the muscles forming the erector spinae - a muscle complex consisting of several smaller intrinsic deep back muscle groups that all together form the intermediate layer of the deep back muscles. The other two groups are the longissimus and iliocostalis muscles. The erector spinae muscles run along the length of the spine , and the spinalis is the most medial of the three erector spinae muscles. The spinalis mainly stretches between the spinous processes of the cervical and thoracic vertebrae, although its upper aspect is also attached to the occipital bone. The spinalis muscle is composed of three parts, and all portions are named based on their location - spinalis capitis , spinalis cervicis and spinalis thoracis muscles. All parts share one common feature - they are innervated by the lateral branches of the dorsal rami of the spinal nerves. Bilateral contractions - extension of head and neck.
Dr bashir ahmadi
About Contact Privacy. Similarly, the spinalis capitis segment stretches from T2 to the occiput and also affects the cervical vertebrae. The spinalis thoracis section is involved in trunk extension. Dorsal branches of the posterior intercostal artery, deep cervical artery, muscular branches of vertebral artery. The opposite of neck extension is neck flexion. Laterally: Flex the head and neck to the same side. But opting out of some of these cookies may affect your browsing experience. You also have the option to opt-out of these cookies. Any cookies that may not be particularly necessary for the website to function and is used specifically to collect user personal data via analytics, ads, other embedded contents are termed as non-necessary cookies. This article includes a list of general references , but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. Necessary Necessary.
Search site Search Search. Go back to previous article.
Spinalis dorsi, the medial continuation of the sacrospinalis , is scarcely separable as a distinct muscle. Cookies allow us to analyze and store information such as the characteristics of your device as well as certain personal data e. Attachments: Arises from the lower thoracic and lumbar vertebrae, sacrum, posterior aspect of the iliac crest, and the sacroiliac and supraspinous ligament. The opposite of neck extension is neck flexion. This article incorporates text in the public domain from page of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy The spinalis capitis muscle originates from the spinous processes of C6 to T2 or the associated nuchal ligament and inserts onto the occiput. Other spinalis muscles not visible. Therefore, some authors use the compound name "thoracic and cervical spinal and semispinal muscle" to describe this muscular complex. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations. This website uses cookies. Recent searches. In Authority control databases Terminologia Anatomica. Acts bilaterally to extend the vertebral column and Innervation: Posterior rami of the spinal nerves.

0 thoughts on “Spinalis origin and insertion”