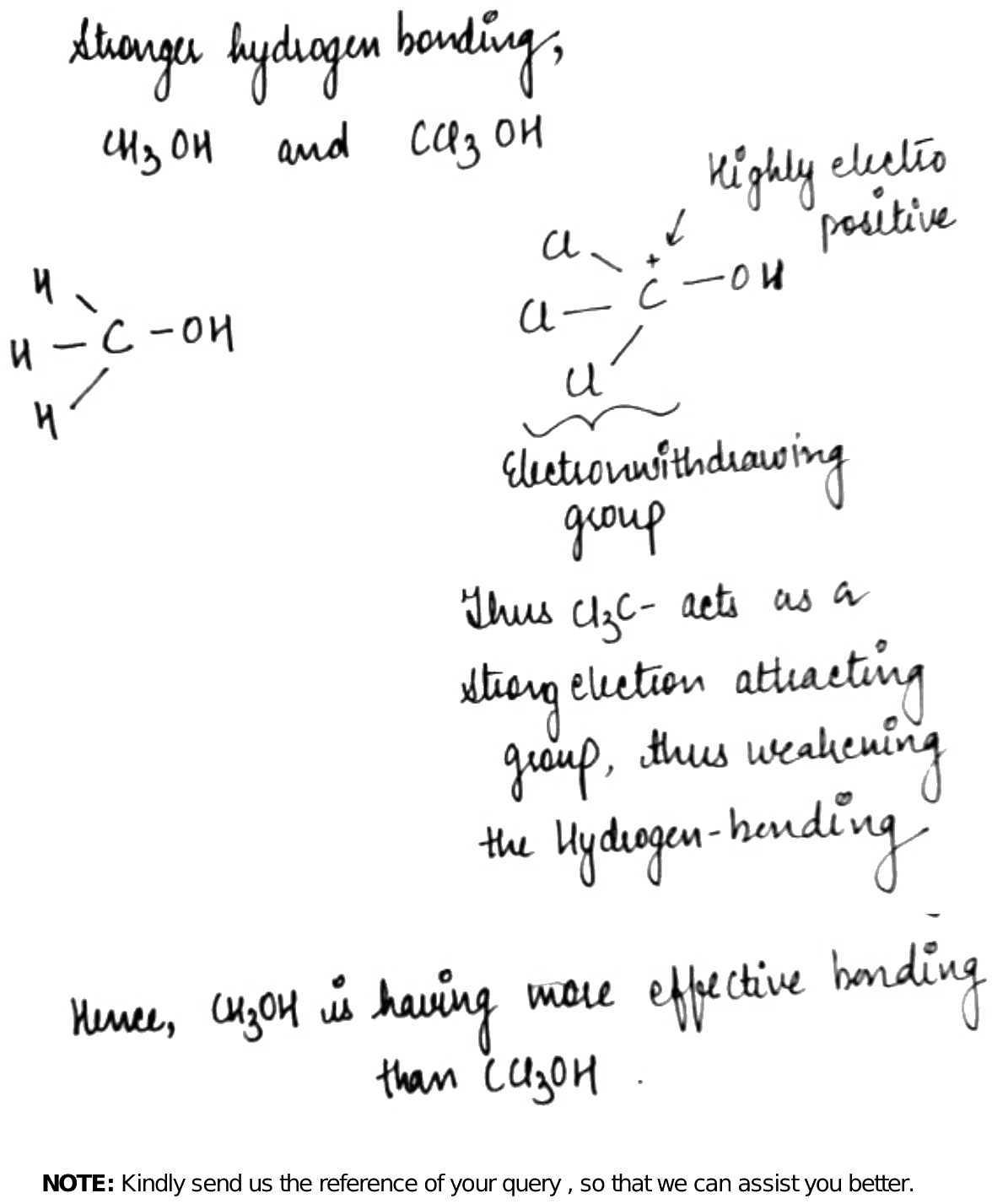
Strongest hydrogen bond is present in
The formation of hydrogen bonds, a sort of attractive intermolecular force induced by the dipole-dipole interaction between a hydrogen atom bound to a strongly electronegative atom and another strongly electronegative atom nearby, is referred to as hydrogen bonding. The interaction between the electronegativity of the bound atom and hydrogen determines the strength of the hydrogen bond.
In chemistry , a hydrogen bond or H-bond is primarily an electrostatic force of attraction between a hydrogen H atom which is covalently bonded to a more electronegative "donor" atom or group Dn , and another electronegative atom bearing a lone pair of electrons—the hydrogen bond acceptor Ac. Hydrogen bonds can be intermolecular occurring between separate molecules or intramolecular occurring among parts of the same molecule. This type of bond can occur in inorganic molecules such as water and in organic molecules like DNA and proteins. Hydrogen bonds are responsible for holding materials such as paper and felted wool together, and for causing separate sheets of paper to stick together after becoming wet and subsequently drying. The hydrogen bond is also responsible for many of the physical and chemical properties of compounds of N, O, and F that seem unusual compared with other similar structures. In a hydrogen bond, the electronegative atom not covalently attached to the hydrogen is named the proton acceptor, whereas the one covalently bound to the hydrogen is named the proton donor. Liquids that display hydrogen bonding such as water are called associated liquids.
Strongest hydrogen bond is present in
.
Access free live classes and tests on the app.
.
A hydrogen bond is an intermolecular force IMF that forms a special type of dipole-dipole attraction when a hydrogen atom bonded to a strongly electronegative atom exists in the vicinity of another electronegative atom with a lone pair of electrons. Intermolecular forces IMFs occur between molecules. Other examples include ordinary dipole-dipole interactions and dispersion forces. Hydrogen bonds are are generally stronger than ordinary dipole-dipole and dispersion forces, but weaker than true covalent and ionic bonds. Many elements form compounds with hydrogen. If you plot the boiling points of the compounds of the group 14 elements with hydrogen, you find that the boiling points increase as you go down the group. The increase in boiling point happens because the molecules are getting larger with more electrons, and so van der Waals dispersion forces become greater. If you repeat this exercise with the compounds of the elements in groups 15 , 16, and 17 with hydrogen, something odd happens. Although the same reasoning applies for group 4 of the periodic table, the boiling point of the compound of hydrogen with the first element in each group is abnormally high. These relatively powerful intermolecular forces are described as hydrogen bonds.
Strongest hydrogen bond is present in
A hydrogen bond is a kind of bonding that is present between an atom of hydrogen and a pair of other atoms having a high electronegativity. Hydrogen-bonding used to be competitively weaker than ionic bonding or covalent bonding, but it is stronger than van der Waals forces. Hydrogen bonding can exist in two ways. One is that it can occur between atoms of different molecules or in the atoms of the same molecule. And another one in which atom of the pair, which is also known as donor as it donated electrons mostly fluorine F , nitrogen N , or oxygen O atom , is covalently bonded to a hydrogen atom -FH, -NH, -OH. Its high electron affinity makes the hydrogen atom take on a slight positive charge. The other pairs of atoms, i. F, N, or O, contain an electron pair that is not shared, which provides it with a slight negative charge. To form a bond the donor atom effectively shares its hydrogen with the acceptor atom mainly through electrostatic attraction.
Martingale strategy calculator
In a hydrogen bond, the electronegative atom not covalently attached to the hydrogen is named the proton acceptor, whereas the one covalently bound to the hydrogen is named the proton donor. Thus nylons are more sensitive than aramids , and nylon 6 more sensitive than nylon Hydrogen bonds can be intermolecular occurring between separate molecules or intramolecular occurring among parts of the same molecule. These interactions exist between nitrogen — hydrogen and oxygen —hydrogen centers. Archived from the original on Bibcode : MolPh.. Share via. CiteSeerX Grushka, N. Because water may form hydrogen bonds with solute proton donors and acceptors, it may competitively inhibit the formation of solute intermolecular or intramolecular hydrogen bonds.
In chemistry , a hydrogen bond or H-bond is primarily an electrostatic force of attraction between a hydrogen H atom which is covalently bonded to a more electronegative "donor" atom or group Dn , and another electronegative atom bearing a lone pair of electrons—the hydrogen bond acceptor Ac. Hydrogen bonds can be intermolecular occurring between separate molecules or intramolecular occurring among parts of the same molecule. This type of bond can occur in inorganic molecules such as water and in organic molecules like DNA and proteins.
In these macromolecules, bonding between parts of the same macromolecule cause it to fold into a specific shape, which helps determine the molecule's physiological or biochemical role. The number of hydrogen bonds formed by a molecule of liquid water fluctuates with time and temperature. Bibcode : JPCA.. A symmetric hydrogen bond is a special type of hydrogen bond in which the proton is spaced exactly halfway between two identical atoms. The initial theory of hydrogen bonding proposed by Linus Pauling suggested that the hydrogen bonds had a partial covalent nature. A protein backbone hydrogen bond incompletely shielded from water attack is a dehydron. This type of bifurcated H-bond provides an intrahelical H-bonding partner for polar side-chains, such as serine , threonine , and cysteine within the hydrophobic membrane environments. Chemical Society Reviews. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences. Because water may form hydrogen bonds with solute proton donors and acceptors, it may competitively inhibit the formation of solute intermolecular or intramolecular hydrogen bonds. CiteSeerX In which of the following the hydrogen bond is strongest: a F-H—F b O-H—S c S-H—F d F-H—O Answer: a Explanation: Hydrogen Bonding The formation of hydrogen bonds, a sort of attractive intermolecular force induced by the dipole-dipole interaction between a hydrogen atom bound to a strongly electronegative atom and another strongly electronegative atom nearby, is referred to as hydrogen bonding.

You are not right. I can prove it.
Certainly. All above told the truth. We can communicate on this theme.
Such did not hear