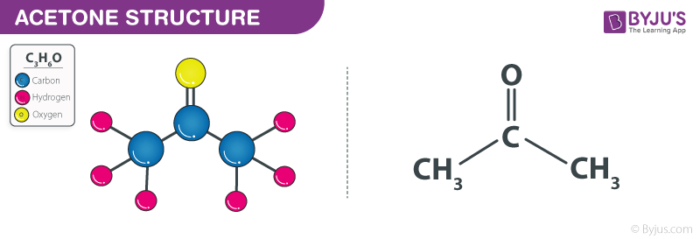
Structure of propanone
We are working on a new version of ChemSpider — if you want to try the new interface go to beta.
Acetone 2-propanone or dimethyl ketone is an organic compound with the formula CH 3 2 CO. It is a colorless, highly volatile and flammable liquid with a characteristic pungent odor. Acetone is miscible with water and serves as an important organic solvent in industry, home, and laboratory. About 6. It serves as a solvent in household products such as nail polish remover and paint thinner. Acetone is produced and disposed of in the human body through normal metabolic processes. It is normally present in blood and urine.
Structure of propanone
.
PubChem CID. SRI consulting.
.
We are working on a new version of ChemSpider — if you want to try the new interface go to beta. Simple Structure Advanced History. Comment on this record. Featured data source. Dimethyl formaldehy de. Dimethyl ketone.
Structure of propanone
Drinking methanol is harmful, not because of the CH 3 OH molecules themselves, but rather because the human body converts these molecules into methanal formaldehyde molecules by combination with oxygen:. Formaldehyde, H 2 CO, is very reactive—in the pure state it can combine explosively with itself, forming much larger molecules. Consequently it is prepared commercially as a water solution, formalin, which contains about 35 to 40 percent H 2 CO. It is used as a preservative for biological specimens, in embalming fluids, and as a disinfectant and insecticide—not a very good substance to introduce into your body. The biggest commercial use of formaldehyde is manufacture of Bakelite, melamine, and other plastics. The functional group found in formaldehyde is called a carbonyl group. Two classes of compounds may be distinguished on the basis of the location of the carbonyl group. In aldehydes it is at the end of a carbon chain and has at least one hydrogen attached.
Streamz
Sausalito, CA. Bibcode : ExFl Gas-chromatographische Charakterisierung organischer Verbindungen. Download as PDF Printable version. Journal of Physical Chemistry. D Y. Although itself flammable , acetone is used extensively as a solvent for the safe transportation and storage of acetylene , which cannot be safely pressurized as a pure compound. It is critical in the Jones oxidation. Studyguide for Techniques and Experiments for Organic Chemistry. Organic compound CH3 2CO ; simplest ketone. Retrieved 2 September NIST Spectra nist ri Bibcode : JBR LC 50 median concentration.
Acetone 2-propanone or dimethyl ketone is an organic compound with the formula CH 3 2 CO.
Although itself flammable , acetone is used extensively as a solvent for the safe transportation and storage of acetylene , which cannot be safely pressurized as a pure compound. Acetone occurs naturally as part of certain metabolic processes in the human body, and has been studied extensively and is believed to exhibit only slight toxicity in normal use. After that time, during World War I , acetone was produced using acetone-butanol-ethanol fermentation with Clostridium acetobutylicum bacteria , which was developed by Chaim Weizmann later the first president of Israel in order to help the British war effort, [24] in the preparation of Cordite. The technique, called acetone vapor bath smoothing, involves placing the printed part in a sealed chamber containing a small amount of acetone, and heating to around 80 degrees Celsius for ten minutes. Industrial organic chemicals. Canadian Centre for Occupational Health and Safety. Structure-retention index relationship on polar columns, J. Miscible [10]. PMC Comment on this record. The conversion of acetone to a polyketal PKA would be analogous to the formation of paraformaldehyde from formaldehyde , and of trithioacetone from thioacetone.

It is not pleasant to you?