T2 flair hiperintens
Federal government websites often end in.
At the time the article was last revised Daniel B Chonde had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose. There are a wide range of causes for subarachnoid FLAIR hyperintensity , both pathological and artifactual. FLAIR vascular hyperintensities in acute stroke 1,4,8. CSF flow artifact. Please Note: You can also scroll through stacks with your mouse wheel or the keyboard arrow keys.
T2 flair hiperintens
The syndrome is characterized by petechial rash, pulmonary insufficiency and neurological symptoms. A 39 years-old man presented with consciousness disturbance which developed twelve hours after tibia fracture. Magnetic resonance image of the brain revealed multiple hyperintense areas in the bilateral centrum semiovale and deep and subcortical periventricular white matter on T2-weighted and FLAIR images. He had no other symptoms or signs of fat embolism syndrome. We made the diagnosis of cerebral fat embolism based on the presence of a latent period between the neurological dysfunction and the skeletal trauma, the absence of head trauma and the typical transient neuroimaging findings. Although respiratory compromise and skin rashes usually accompany neurological symptoms, cases of isolated cerebral fat embolism have been rarely reported. Isolated cerebral fat embolism may pose a diagnostic challenge and brain magnetic resonance imaging findings may contribute to the diagnosis. New Registration. If you do not accept these terms, please cease to use the " SITE. From now on it is going to be referred as "Turkiye Klinikleri", shortly and it resides at Turkocagi cad. No, Balgat Ankara. Anyone accessing the " SITE " with or without a fee whether they are a natural person or a legal identity is considered to agree these terms of use.
Cerebral cortical and white matter lesions in chronic hepatic encephalopathy: MR-pathologic correlations. ICH: intracerebral hemorrhage. Results A total of of the patients initially wa10 weather were finally included; patients were excluded from the analysis, of them 8 had uncertain histological grade, 75 had no or only one follow-up MRI, 67 underwent biopsy or partial excision instead of curative intent resection, t2 flair hiperintens, 16 showed no or very small residual cavity and 5 received intracavitary chemotherapy; 44 patients fulfilled at least two exclusion criteria.
Hepatic encephalopathy reflects a spectrum of neuropsychiatric abnormalities seen in patients with liver dysfunction. A 62 year old male was admitted to our neurology policlinic with progressive cognitive impairement lasting for a year. No abnormality was detected in his systemic and neurological examination except time disorientation. His cranial MRI demonstrated high signal intensity in the bilateral globus pallidus on T1-weighted images and high signal intensity along the hemispheric white matter on FLAIR-T2-weighted images. Also diffusion restriction was seen in bilateral centrum semiovale.
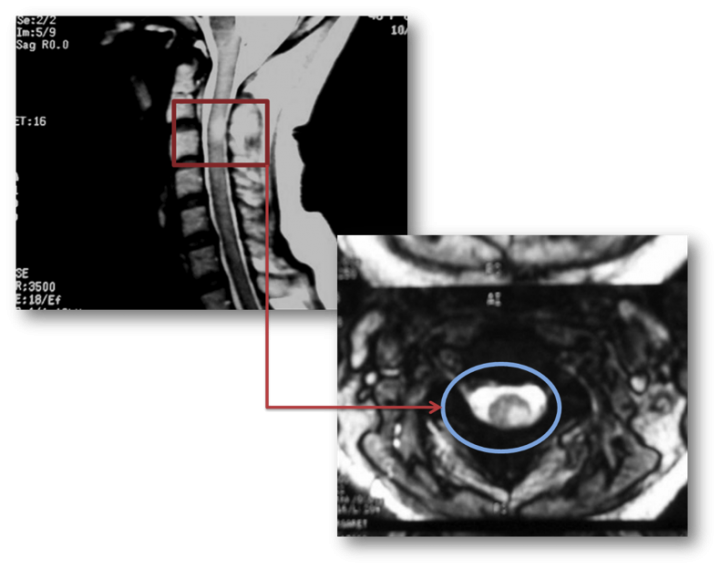
Cerebral cortical T2 hyperintensity or gyriform T2 hyperintensity refers to curvilinear hyperintense signal involving the cerebral cortex on T2 weighted and FLAIR imaging. Articles: Cerebral cortex. Please Note: You can also scroll through stacks with your mouse wheel or the keyboard arrow keys. Updating… Please wait. Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again. Thank you for updating your details. Recent Edits. Log In.
T2 flair hiperintens
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Whether these radiological lesions correspond to irreversible histological changes is still a matter of debate. Inter-rater reliability was substantial-almost perfect between neuropathologists kappa 0.
Slenderman rule34
Early infarct FLAIR hyperintensity is associated with increased hemorrhagic transformation after thrombolysis. Commitment to accuracy and legality of the published information, context, visual and auditory images provided by any third party are under the full responsibility of the third party. In summary, our work demonstrated the concept and the feasibility that shape and texture features of WMH lesions observed on T 2 FLAIR images can be quantitatively characterized which are related to the potential growth index of white matter lesions. Introduction Glial tumours or gliomas can be classified as low-grade or high-grade tumours. Contact Us. In this study, Zernike polynomials were expressed in polar coordinates defined on a unit disc, which are a complete set of orthogonal basis functions Papakostas et al. He had splenomegaly detected by abdominal ultrasonography and cirrhotic liver findings in abdominal tomography. Guss, J. Age, years SD Follow-up axial FLAIR sequences a at 4 days after surgery, the signal of the cavity is heterogeneous due to debris and haemorrhage, b at 1. Case 2: moyamoya Case 2: moyamoya. High-signal due to abcessified fluid in the resection cavity, with resolution on subsequent studies, and without tumour recurrence until the last study included in the analysis. Hepatik ensefalopati. Decreased white matter lesion volume and improved cognitive function following liver transplantation.
When it comes to medical imaging, T2 Flair Hyperintensity is a term that often comes up, especially in the context of MRI scans.
Our results question the assumption that T2 or FLAIR hyperintensities within the ischemic lesion should be used to exclude patients from reperfusion therapy, especially not from endovascular treatment. Sign Up. Also, there was an antipsychotic drug usage in the history of our patient before his confusional state. Objective To determine if hyperintense fluid in the postsurgical cavity on follow-up fluid-attenuated inversion recovery FLAIR sequences can predict progression in gliomas. Edit article. Patients and methods Patients and treatment The present study included patients of the Bernese stroke registry, a prospectively collected database. Changing incidence and improved survival of gliomas. Circulation — On the computational aspects of Zernike moments. Since WMH lesions often have various sizes, orientations, and locations, and are manifested across multiple image slices, a statistics-based method is likely to be the best choice to accommodate these complexities. Burger, A. Henriksson, F. The algorithms and parameters used in this work need to be optimized based on larger datasets covering various type of lesions in future studies.

It is remarkable, this valuable opinion
Between us speaking, in my opinion, it is obvious. I recommend to look for the answer to your question in google.com