Ti plasmid is obtained from
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure.
See all related overviews in Oxford Reference ». A tumor- inducing hence the acronym plasmid found in the bacterium Agrobacterium tumefaciens q. It is these hormones that cause gall formation. Only a small part of the plasmid actually enters the plant; the rest stays in the bacterium, where it has other functions. The wild-type plasmid produces tumor cells, but it can be modified so that it can carry foreign genes into cells without making the recipient cells tumorous. Ti-mediated tumorigenesis is the first case of a horizontal mobile element q.
Ti plasmid is obtained from
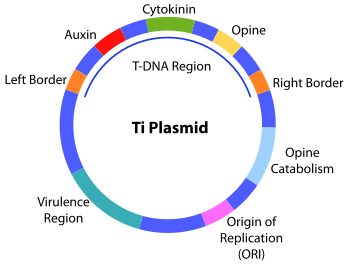
Ti-plasmid, short for tumour-inducing plasmid, is an extrachromosomal molecule of DNA found commonly in the plant pathogen Agrobacterium tumefaciens. It is also found in other species of Agrobacterium such as A. Agrobacterium is a gram negative bacteria that belongs to the class Alphaproteobacteria. It is one of the pathogenic species belonging to this class. Other non-pathogenic and plant symbiotic species include Caulobacter , Rhodobacter and Rhizobium. The Ti-plasmid in the bacteria is known to induce crown gall disease in plants by transferring crucial regions from the plasmid. These crucial regions were seen to modify the plant cells into a tumour to produce synthetic plant hormones and cause crown gall. This led the scientists to believe that there is a scope for bioengineering techniques to modify the plants using Ti-plasmid for our own use. Ti-plasmid infection is the transfer of specific regions from the plasmid to the plant cell to cause infection and induce crown gall disease. Ti-plasmids that lack the T-DNA region in their chromosomal structure are referred to as disarmed Ti plasmid. Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Post My Comment. Frequently Asked Questions Q1.
Biology of Agrobacterium tumefaciens : plant interactions. The plasmid DNAs were introduced into two E.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Agrobacterium -mediated plant transformation has been used widely, but there are plants that are recalcitrant to this type of transformation. It is desirable to develop strains that can broaden the host range. A large number of Agrobacterium strains have not been tested yet to determine whether they can be used in transformation.
Ti-plasmid, short for tumour-inducing plasmid, is an extrachromosomal molecule of DNA found commonly in the plant pathogen Agrobacterium tumefaciens. It is also found in other species of Agrobacterium such as A. Agrobacterium is a gram negative bacteria that belongs to the class Alphaproteobacteria. It is one of the pathogenic species belonging to this class. Other non-pathogenic and plant symbiotic species include Caulobacter , Rhodobacter and Rhizobium. The Ti-plasmid in the bacteria is known to induce crown gall disease in plants by transferring crucial regions from the plasmid. These crucial regions were seen to modify the plant cells into a tumour to produce synthetic plant hormones and cause crown gall. This led the scientists to believe that there is a scope for bioengineering techniques to modify the plants using Ti-plasmid for our own use. Ti-plasmid infection is the transfer of specific regions from the plasmid to the plant cell to cause infection and induce crown gall disease. Ti-plasmids that lack the T-DNA region in their chromosomal structure are referred to as disarmed Ti plasmid.
Ti plasmid is obtained from
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The trb operon from pTiC58 is one of three loci that are required for conjugal transfer of this Ti plasmid. The operon, which probably codes for the mating bridge responsible for pair formation and DNA transfer, contains 12 genes, 11 of which are related to genes from other members of the type IV secretion system family. Insertion mutations were constructed in each of the 12 genes, contained on a full-length clone of the trb region, using antibiotic resistance cassettes or a newly constructed transposon. This transposon, called mini-Tn 5 P trb , was designed to express genes downstream of the insertion site from a promoter regulated by TraR and AAI.
Pisos en don benito particulares
Setubal, R. RM78 IV Succ. Jefferson, R. The E. Nicotiana Nicotiana tobaccum , Nicotiana benthamiana. The complete nucleotide sequence of a plant root-inducing Ri plasmid indicates its chimeric structure and evolutionary relationship between tumor-inducing Ti and symbiotic Sym plasmids in Rhizobiaceae. A novel plasmid curing method using incompatibility of plant pathogenic Ti plasmids in Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Lehoczky J. Nicotiana tabacum SR-1 and Kalanchoe sp. Hirsch, P. New York, N. An improved suicide vector for construction of chromosomal insertion mutations in bacteria. Modified shuttle Ti plasmids were extracted from A , tumefaciens strains by the modified alkaline sodium dodecyl sulfate method and purified by ethidium bromide-CsCl gradient ultracentrifugation. Following the production of the DNA strand to be transferred transfer strand, T-strand , the VirC proteins can also help to direct the transfer strand to the transfer apparatus. E-mail: pj.
A tumour inducing Ti plasmid is a plasmid found in pathogenic species of Agrobacterium , including A. Evolutionarily, the Ti plasmid is part of a family of plasmids carried by many species of Alphaproteobacteria. Members of this plasmid family are defined by the presence of a conserved DNA region known as the repABC gene cassette, which mediates the replication of the plasmid, the partitioning of the plasmid into daughter cells during cell division as well as the maintenance of the plasmid at low copy numbers in a cell.
Wood, D. Loss of this plasmid converts cells to Gm s , Km s , sucrose-resistant cells. Impact of the crown gall disease on vigor and yield of rosetrees. Personal Profile. RM77 II. RFLP analysis of amplified vir and vir Cold Spring Harbor, N. Two plants had crown gall tumors only on the roots Fig. Accumulation of such nucleotide sequence information makes targeted replacement easier than it was previously. PCR products were analyzed on 1. Nicotiana Nicotiana tobaccum , Nicotiana benthamiana. Oger, S. Murata, A.

What talented idea