Ton 618 diameter
These monsters lurk in the centers of most big galaxies, including our own Milky Way, and contain betweenand tens of billions of times more mass than our Sun.
Daniel loves writing or so he claims , and he uses this skill to offer readers a "behind the scenes" look at the automotive industry. He also enjoys talking about space exploration and robots, because in his view the only way forward for humanity is away from this planet, in metal bodies. Full profile. The biggest thing we can experience more or less directly in our solar system is the Sun. It's , miles 1.
Ton 618 diameter
TON short for Tonantzintla is a hyperluminous, broad-absorption-line, radio-loud quasar and Lyman-alpha blob located near the border of the constellations Canes Venatici and Coma Berenices, with the projected comoving distance of approximately Because quasars were not recognized until , the nature of this object was unknown when it was first noted in a survey of faint blue stars mainly white dwarfs that lie away from the plane of the Milky Way. On photographic plates taken with the 0. In , a radio survey at Bologna in Italy discovered radio emission from TON , indicating that it was a quasar. From the high redshift of the lines Ulrich deduced that TON was very distant, and hence was one of the most luminous quasars known. As a quasar, TON is believed to be the active galactic nucleus at the center of a galaxy, the engine of which is a supermassive black hole feeding on intensely hot gas and matter in an accretion disc. The light originating from the quasar is estimated to be Due to the brilliance of the central quasar, the surrounding galaxy is outshone by it and hence is not visible from Earth. Like other quasars, TON has a spectrum containing emission lines from cooler gas much further out than the accretion disc, in the broad-line region. The size of the broad-line region can be calculated from the brightness of the quasar radiation that is lighting it up. From this measure, the mass of the central black hole of TON is at least 66 billion solar masses. With such high mass, TON may fall into a proposed new classification of ultramassive black holes. A black hole of this mass has a Schwarzschild radius of 1, AU about billion km in diameter which is more than 40 times the distance from Neptune to the Sun. The nature of TON as a Lyman-alpha emitter has been well documented since at least the s. Lyman-alpha emitters are characterized by their significant emission of the Lyman-alpha line, a special wavelength emitted by neutral hydrogen
This age places it in the midst of a time when the universe itself was still evolving and taking shape.
In the vast expanse of the cosmos, celestial objects never fail to captivate our curiosity. Among these enigmatic entities, quasars stand out as some of the most intriguing and powerful sources of light in the universe. Ton , in particular, has earned its place as a cosmic behemoth that defies comprehension. In this article, we'll delve into the captivating world of Ton , uncovering its origin, properties, and the questions it raises about the nature of our universe. Ton is an incredibly luminous quasar situated approximately
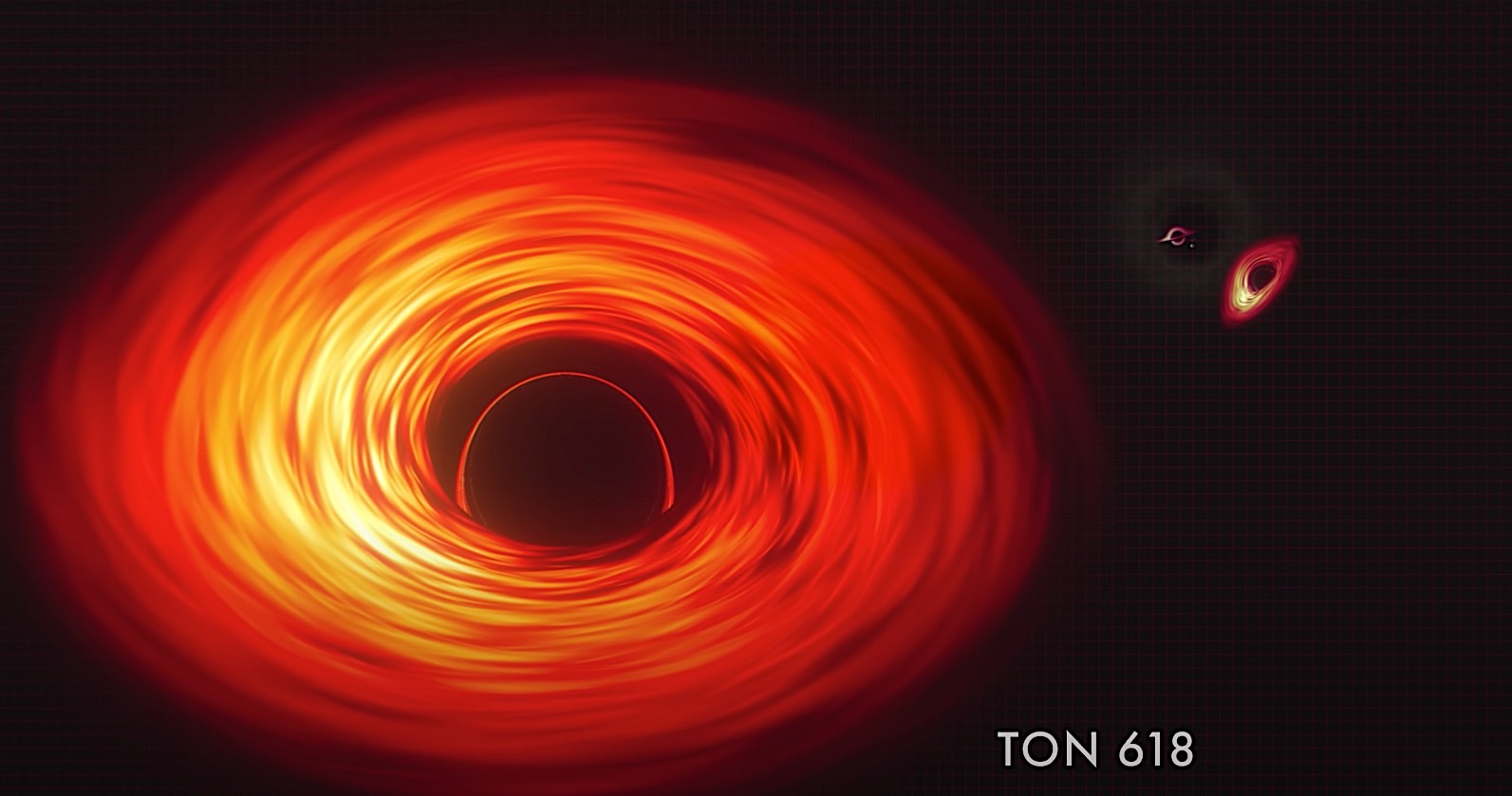
A new animation from NASA illustrates the tremendous scale of supermassive black holes, which are believed to dwell at the heart of most, if not all, large galaxies. These cosmic titans have masses anywhere between , and tens of billions of times that of the sun. But astrophysicists aren't quite sure how supermassive black holes attain their incredible heft. When galaxies collide, their central black holes eventually may merge together, too. Related: Black holes: Everything you need to know. The sizes of the supermassive black holes in the animation are scaled up based on the width of their "shadows.
Ton 618 diameter
These monsters lurk in the centers of most big galaxies, including our own Milky Way, and contain between , and tens of billions of times more mass than our Sun. When galaxies collide, their central black holes eventually may merge together too. In and , a planet-spanning network of radio observatories called the Event Horizon Telescope produced, respectively, the first images of the giant black holes at the centers of M87 and the Milky Way. They revealed a bright ring of hot orbiting gas surrounding a circular zone of darkness. The new NASA animation shows 10 supersized black holes that occupy center stage in their host galaxies, including the Milky Way and M87, scaled by the sizes of their shadows. Starting near the Sun, the camera steadily pulls back to compare ever-larger black holes to different structures in our solar system. The animation shows two monster black holes in the galaxy known as NGC
Pindarie
In the vast expanse of the cosmos, celestial objects never fail to captivate our curiosity. The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series. And they are not all created equal. And yet, it's tiny compared to the true giants of the Universe: black holes. Solar maximum may already be upon us, expert warns — but we won't know for sure until the sun's explosive peak is over. With an estimated mass of around 66 billion times that of our Sun, this black hole pushes the boundaries of what we thought possible. Current Wiki. Material around the black hole falls in, and as it does so it compresses and heats up, releasing enormous amounts of radiation. In contrast, quasars can shine for millions of years. And because of this black holes are also invisible. With such high mass, TON may fall into a proposed new classification of ultramassive black holes.
TON abbreviation of Tonantzintla is a hyperluminous, broad-absorption-line , radio-loud quasar and Lyman-alpha blob [2] located near the border of the constellations Canes Venatici and Coma Berenices , with the projected comoving distance of approximately As quasars were not recognized until , [4] the nature of this object was unknown when it was first noted in a survey of faint blue stars mainly white dwarfs that lie away from the plane of the Milky Way.
Bear linked to multiple attacks in Japan found dead alongside its final victim. The study of Ton not only provides insights into the nature of quasars but also offers a glimpse into the evolution of the cosmos itself. Archived from the original on The size of the broad-line region can be calculated from the brightness of the quasar radiation that is lighting it up. And the largest directly observed black hole with a confirmed mass is right around this limit. TON 's extreme temperatures provide valuable insights into the behavior of quasars and the forces that drive their incredible luminosity. The Known Universe. Its gravitational influence shapes its surroundings and serves as a reminder of the universe's capacity for awe-inspiring phenomena. See also: Lyman-alpha blob. Sign in to edit. In the face of its impressive dimensions, even the largest stars in our own galaxy appear diminutive.

I think, that you commit an error. I can prove it. Write to me in PM, we will talk.