Tonights sky
But many of our greatest discoveries start with the simple act of observing. Jupiter plows through the Pleiades on March 14, tonights sky, a chance to spot Mercury tonights sky month's end along with a subtle lunar eclipse, and a comet worth keeping an eye on!
This organized Observing Guide is designed to provide key information for planning observing sessions of Solar System Objects from your location. The webpage is divided into three distinct sections, offering an overview of celestial objects visible during specific time intervals: post-sunset observations, nocturnal observations, pre-sunrise observations. Additional useful tools that you can consider when planning your observation sessions are the Online Sky Map and Planetarium and the list of Celestial Objects Visible Now. In astronomy a conjunction is defined as a close apparent alignment in the sky between two or more celestial bodies. Here we list, the closest conjunctions happening between objects we are currently tracking, in order of increasing separation. The green arrow indicates that the objects are currently getting closer, while the red arrow means that the objects are increasing their apparent separation. We use cookies to deliver essential features and to measure their performance.
Tonights sky
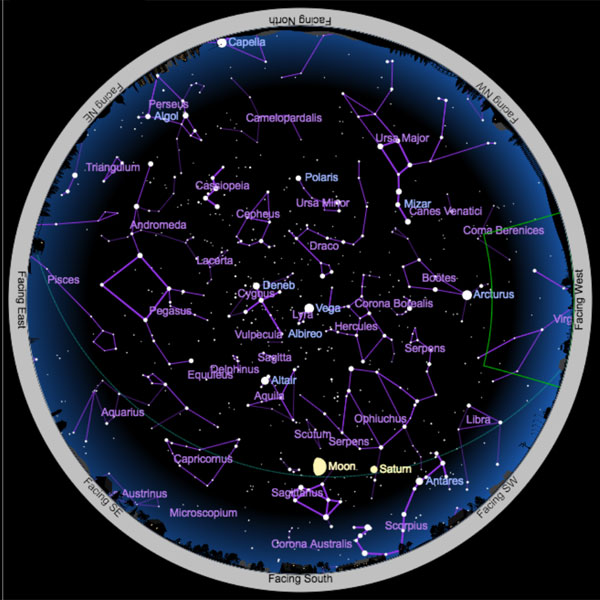
March All descriptions below are for mid-northern latitudes in the Northern Hemisphere. For more about the giant planet Jupiter in the evening sky this month visit: Spot the King of Planets: Observe Jupiter. Back to top of page. To dig deeper into the March evening sky check out the video below from the Space Telescope Science Institute. Go to Full Screen for best viewing. To do more constellation hunting visit these pages and have some fun! Last Quarter Moon rises in the middle of the night, is visible in the early morning sky before sunrise, and sets around mid-day. First Quarter Moon rises mid-day, is visible in the early evening sky, and sets in the middle of the night. Visit The Moon for more about why the Moon changes shape throughout the month.
Daytime skywatching: On the days surrounding first quarter, the moon is visible in the afternoon daytime sky. Binoculars will reveal Jupiter's four large Galilean moons flanking the planet on any night. On March 13 the waxing crescent moon will shine below Uranus beside Jupiter, tonights sky.
Helping the amateur astronomer plan their night by showing what you can see and what it will look like. Welcome to Tonight's Sky. Tonight's Sky's mission is to provide an online tool for amateur astronomers to plan their observing sessions. The site will generate a list of visible objects based on your criteria with links to help you plan your observing session and research your targets. A list of objects will be produces based on your inputs that are visible at your location when you plan to observe.
This organized Observing Guide is designed to provide key information for planning observing sessions of Solar System Objects from your location. The webpage is divided into three distinct sections, offering an overview of celestial objects visible during specific time intervals: post-sunset observations, nocturnal observations, pre-sunrise observations. Additional useful tools that you can consider when planning your observation sessions are the Online Sky Map and Planetarium and the list of Celestial Objects Visible Now. In astronomy a conjunction is defined as a close apparent alignment in the sky between two or more celestial bodies. Here we list, the closest conjunctions happening between objects we are currently tracking, in order of increasing separation. The green arrow indicates that the objects are currently getting closer, while the red arrow means that the objects are increasing their apparent separation. We use cookies to deliver essential features and to measure their performance. By using this site you accept our Privacy Policies. Got It!
Tonights sky
Helping the amateur astronomer plan their night by showing what you can see and what it will look like. Welcome to Tonight's Sky. Tonight's Sky's mission is to provide an online tool for amateur astronomers to plan their observing sessions. The site will generate a list of visible objects based on your criteria with links to help you plan your observing session and research your targets. A list of objects will be produces based on your inputs that are visible at your location when you plan to observe. Any object below the local horizon will be excluded.
Thedonato
In astronomy a conjunction is defined as a close apparent alignment in the sky between two or more celestial bodies. Utility Menu News Events Intranet. Its position on the far side of the sun from Earth will give the planet a rather small 5 arc-seconds-wide disk in telescopes. That constellation's brightest stars , golden Pollux and brighter, whiter Castor above it should still be visible against the moon's glare. Why and when do conjunctions happen? As the night wears on, the moon's orbital motion will carry it towards Pollux, while the diurnal rotation of the sky shifts the constellation to the moon's right or celestial northwest. For several nights surrounding Friday, March 15, the moon's brightly lit southeastern limb will be rotated toward Earth, revealing a collection of dark patches that can be seen in a backyard telescope. In Greek mythology, the stars are named for the daughters of Atlas and Pleione. Looking for a telescope for the next night sky event? Like nearby Jupiter, Uranus will be observable in the western sky during early evening during March; but its steadily decreasing angle from the sun will shorten our telescope time with it. Since sunlight can only shine on the far side of a new moon, and the moon is in the same region of the sky as the sun, our natural satellite becomes completely hidden from view for about a day — unless a solar eclipse occurs! Above the southeastern horizon for about an hour before sunrise on Thursday, March 7, the old crescent moon will be shining two fist diameters to the right or 18 degrees to the celestial WSW of the brilliant planet Venus. The full moon dims slightly during a penumbral lunar eclipse tonight, as it passes through the outer part of Earth's shadow, the penumbra. EDT or p. For planet visibility in the coming night, please check again after 12 noon.
The Earth-Moon distance from the center of the Earth to the center of the Moon will reach a minimum of , km , miles.
Sky chart showing Jupiter with the Moon on the evening of March 13, one hour after sunset. If you're stuck in a city or suburban area, use a tree or dark building to block ambient light or moonlight and help reveal fainter sky objects. And on March 13th, it's joined by a crescent Moon so close that the pair will be visible together through binoculars. For southerly latitude observers that can see Mars in a dark sky, it will travel east through Capricornus until March 19 and then enter Aquarius. Its location is only 8. Three prominent craters break up the expanse of Oceanus Procellarum, the broad dark region on the left-hand western half of the moon. Visibility improves as the sunlight fades. Got It! Referrers and Web Rings. You can find it low in the west-northwest part of the sky at the end of evening twilight.

It is excellent idea
I shall simply keep silent better