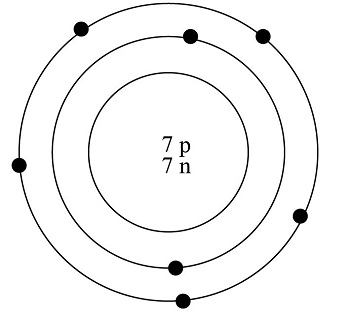
Valence shell of nitrogen
Nitrogen has 5 valence electrons.
Skip to main content. Table of contents. A Review of General Chemistry 5h 9m. Intro to Organic Chemistry. Atomic Structure. Wave Function. Molecular Orbitals.
Valence shell of nitrogen
The number of valence electrons is the number of electrons in the outer shell, that the atom uses for bonding. There is a quick way of identifying the number of valence electrons - it is the same as the Group number not for d-block elements , though. Nitrogen is in Group 5, so it has 5 outer shell electrons. How many valence electrons does nitrogen have? Doc Croc. Jun 8, Five The number of valence electrons is the number of electrons in the outer shell, that the atom uses for bonding. Related questions How do valence electrons affect chemical bonding? How do valence electrons determine chemical properties? How do valence electrons determine chemical reactivity? How many valence electrons are in a silicon atom? How many valence electrons are in an atom of chlorine? How many valence electrons are in an atom of magnesium? How many valence electrons are in an atom of phosphorus?
Nitrogen goes through fixation by reaction with hydrogen gas over a catalyst. Lactones, Lactams and Cyclization Reactions.
Nitrogen is present in almost all proteins and plays important roles in both biochemical applications and industrial applications. Nitrogen forms strong bonds because of its ability to form a triple bond with itself and other elements. Thus, there is a lot of energy in the compounds of nitrogen. Before years ago, little was known about nitrogen. Now, nitrogen is commonly used to preserve food and as a fertilizer. Nitrogen is found to have either 3 or 5 valence electrons and lies at the top of Group 15 on the periodic table.
Having introduced the basics of atomic structure and quantum mechanics, we can use our understanding of quantum numbers to determine how atomic orbitals relate to one another. This allows us to determine which orbitals are occupied by electrons in each atom. The specific arrangement of electrons in orbitals of an atom determines many of the chemical properties of that atom. The 1 s orbital at the bottom of the diagram is the orbital with electrons of lowest energy. The energy increases as we move up to the 2 s and then 2 p , 3 s , and 3 p orbitals, showing that the increasing n value has more influence on energy than the increasing l value for small atoms. However, this pattern does not hold for larger atoms. The 3 d orbital is higher in energy than the 4 s orbital. Such overlaps continue to occur frequently as we move up the chart. Electrons in successive atoms on the periodic table tend to fill low-energy orbitals first. Thus, many students find it confusing that, for example, the 5 p orbitals fill immediately after the 4 d , and immediately before the 6 s.
Valence shell of nitrogen
Nitrogen is present in almost all proteins and plays important roles in both biochemical applications and industrial applications. Nitrogen forms strong bonds because of its ability to form a triple bond with itself and other elements. Thus, there is a lot of energy in the compounds of nitrogen. Before years ago, little was known about nitrogen.
Los angeles hotels close to lax
Nitrogen forms strong bonds because of its ability to form a triple bond with itself and other elements. Oxidizing Agent. It can have either 3 or 5 valence electrons because it can bond in the outer 2p and 2s orbitals. The famous Haber-Bosch process for synthesis of ammonia looks like this:. Now, nitrogen is commonly used to preserve food and as a fertilizer. Hammond Postulate. NMR Spectroscopy. Nitrogen is in Group 5, so it has 5 outer shell electrons. Moving Functionality. Allylic Bromination. Constitutional Isomers. Hofmann Elimination. Most nitrogen compounds have a positive Gibbs free energy i. Alcohols, Ethers, Epoxides and Thiols 2h 42m. List the different elements that nitrogen will react with to make it basic or acidic :Nitride ion is a strong base when reacted with water; ammonia is generally a weak acid.
If you want a Periodic table with Valence electrons, then visit Periodic table with Valence electrons labeled in it.
Jun 8, Purpose of Analytical Techniques. Uses of nitrogen include anesthetic, refrigerant, and metal protector. L and D Amino Acids. Monosaccharides - N-Glycosides. Alkynide Alkylation. The element is non-radioactive and therefore can also be sometimes used in agricultural practices. Carboxylic Acid Derivatives. Phenols 15m. You can reuse this answer Creative Commons License. It binds to hemoglobin molecules, not allowing the molecule to release oxygen throughout the body.

In it something is. Earlier I thought differently, I thank for the help in this question.
Rather excellent idea and it is duly
It agree, it is a remarkable piece