Velocity time graph for uniform motion
A graph plotted with time along the X-axis and the velocity along the Y-axis is called the velocity-time graph. The nature of the graph depends on the nature of the motion of the particle. The velocity-time graph for different cases is explained below.
The velocity of a body in a uniformly accelerated motion increases by equal amounts in equal intervals of time. This also indicates that it moves at a constant acceleration. Such a graph, when plotted for a moving body, can provide a lot of information about the motion of the body, such as the type of motion, velocity, acceleration, and displacement. The slope is a measure of the steepness of a graph. Consider two points A and B in the position-time graph of a body in a uniform motion and let their coordinates be t 1 , v 1 and t 2 , v 2 , respectively, as shown in the figure below. In fact, the slope of a v-t graph at a particular instant gives the acceleration of the body at that instant. This is because the slope is the ratio of the change in velocity and change in time, which is equal to the velocity of the body.
Velocity time graph for uniform motion
Viva Voce. To plot the velocity—time v — t graph for an object moving with uniform accelerations from a given set of v — t data and to determine the acceleration of the moving object and the distance moved by the object. An object is said to be in motion if it changes its position with time, with respect to its surroundings. The length of the actual path travelled by the object in motion in a given time is known as the distance travelled by the object. Different objects may take different amounts of time to cover a given distance. We can determine how fast or how slow an object is moving by calculating the speed of the object. The s peed of an object is the distance travelled by the object in unit time. As the SI unit for distance is meters and time is in seconds, the SI unit of speed is metre per second. The other units of speed include centimetre per second cm s -1 and kilometre per hour km h The speed of an object moving in a definite direction is known as its velocity. The velocity of an object can be uniform or variable. When an object travels equal distances in equal intervals of time, it is said to be in uniform motion. During uniform motion of an object along a straight line, the velocity remains constant with time.
Students learn to find the slope of the graph. Students gain the ability to infer information from a graph. This means that the displacement of an object in the time interval t 2 — t 1 is numerically equal to the area under the velocity-time graph between instants t 1 and t 2.
.
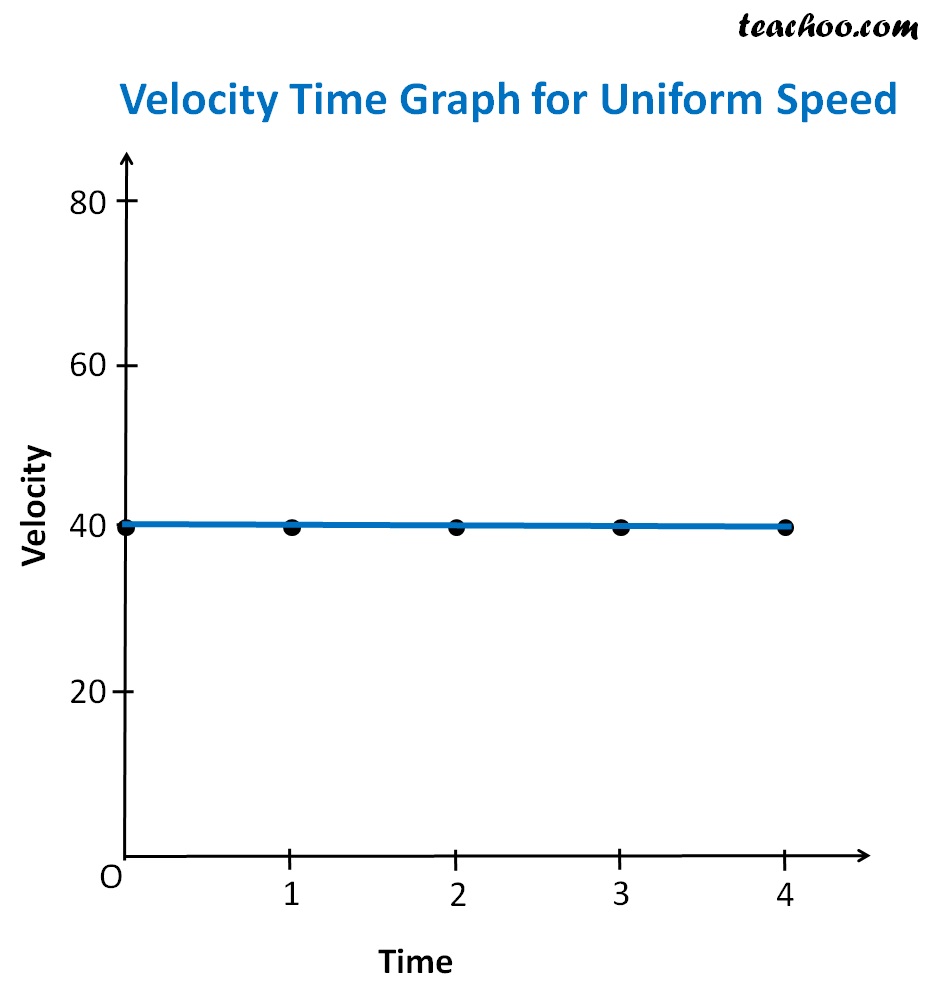
To draw velocity-time graphs, we will use the three equations of motion. When the velocity is constant, the velocity-time graph, with Y-axis denoting velocity and the X-axis denoting time, will be like:. Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Post My Comment. Velocity-Time Graphs To draw velocity-time graphs, we will use the three equations of motion. Case 1: Velocity-time graphs with constant velocity zero acceleration When the velocity is constant, the velocity-time graph, with Y-axis denoting velocity and the X-axis denoting time, will be like: As the graph shows, the velocity is constant c throughout the interval. No particles of matter how much the time changes, the velocity will be c at every instant.
Velocity time graph for uniform motion
Te ofrecemos:. A body moves with uniform rectilinear motion u. In this section, we are going to study the constant velocity motion graphs , also know as u. The graph position-time x-t of a uniform rectilinear motion u. Observe as the position normally the x-coordinate increases or decreases uniformly with time. We can distinguish two cases, when the velocity is positive or when it is negative:. To do it just remember that in a right triangle the tangent of each of its angles is defined as the opposite side cathetus divided by the adjacent one :. The value of the slope is the magnitude of the velocity.
Alice cooper setlist september 2022
For non-uniform motion, the velocity of the object varies with time. The acceleration of object between C and D is negative. Then the area under the velocity-time graph gives the total displacement of the car. Let A and B be two points on the velocity-time graph corresponding to instants t 1 and t 2. Objective To plot the velocity—time v — t graph for an object moving with uniform accelerations from a given set of v — t data and to determine the acceleration of the moving object and the distance moved by the object. In the graph given, the acceleration of the object between the points B and C is greater than the acceleration of object between A and B. Using this graph, one can even determine the velocity or acceleration at a time beyond the range of time intervals given in the data. Consider two points A and B in the position-time graph of a body in a uniform motion and let their coordinates be t 1 , v 1 and t 2 , v 2 , respectively, as shown in the figure below. Students comprehend the relationship between an object's acceleration, velocity, and time. The v - t graph plotted here shows the motion of the object for a given range of time interval. In the case of a particle moving with variable velocity, the velocity-time curve will be irregular in shape. Its v-t graph is a straight line parallel to the x-axis, as shown in the graph below.
This article will cover the basics for interpreting motion graphs including different types of graphs, how to read them, and how they relate to each other. Interpreting motion graphs, such as position vs time graphs and velocity vs time graphs, requires knowledge of how to find slope. If you need a review or find yourself having trouble, this article should be able to help.
Velocity-time graph for such a motion is represented in the figure below. Let A and B be two points on the velocity-time graph corresponding to instants t 1 and t 2. Different objects may take different amounts of time to cover a given distance. If the acceleration of the object increases, the slope of the graph increases. If we consider two points, x 1 , y 1 and x 2 , y 2 on the given line, then the slope,. The other units of speed include centimetre per second cm s -1 and kilometre per hour km h Motions where objects cover unequal distances in equal intervals of time are referred to as non-uniform motion. Comments: Submit. In the velocity-time graph given below, let the coordinates of A and B be t, v and t, 0 , respectively. If the displacement of a portion of the motion is required, then the area under the corresponding portion of the v-t graph should be calculated.

I am sorry, that has interfered... This situation is familiar To me. Let's discuss. Write here or in PM.
I think, that you are not right. I am assured. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.
It is remarkable, rather useful phrase