What are the drawbacks of rutherford model of atom
Rutherford Atomic model is also known as the Rutherford model, nuclear atomor planetary model of the atom was established in the year which explained the structure of atoms and was developed by the New Zealand-born physicist Ernest Rutherford. The model derived that the atom is nothing but a small tiny dense mass that has a positively charged body present in the core which is presently known as the nucleus where the entire mass of the atom is concentrated and around it revolves the negatively charged light electrons at a certain distance much like the planets revolving around the sun. In the gold foil experiment, the nucleus was postulated as a dense and small mass which was responsible for the scattering of the alpha particles, what are the drawbacks of rutherford model of atom. It was observed in a series of experiments that were carried out by the undergraduate Ernest Marsden under the guidance of Rutherford and German physicist Hans Geiger in
Rutherford atomic model was the first step in the evolution of the modern atomic model. Ernest Rutherford was a keen scientist who worked to understand the distribution of electrons in an atom. He performed an experiment using alpha particles and gold foil and made the following observations:. From these conclusions, he calculated that the radius of the nucleus is around 10 5 times less than that of the atom. Rutherford developed a nuclear model of the atom on the basis of his experiment and observations. The Rutherford atomic model has the following features:. As before, the Rutherford atomic model was also challenged and questioned by many.
What are the drawbacks of rutherford model of atom
At that time those hypotheses are considered revolutionary as there was an experiment to back that hypothesis. But as the experiment performed by Rutherford is rudimentary in nature, this model of the atom can be seen with a lot of major drawbacks, all of which we will be learning about under the heading Drawback. Many scientists came up with different ideas and explanations of the structure of an atom such as Thomsom and Bohr. The most classical and accurate model was introduced by the scientist named Ernest Rutherford in the year However, the model did give a brief introduction to what and how the atom is formed. Rutherford explained that an atom is mainly made up of Electrons negatively charged particles and nuclei positively charged particles , and they are arranged in the atom in a fixed manner. The nucleus is positively charged due to the presence of protons the positive charge , apart from the protons, neutrons no charge on them are also present inside the nucleus. It can also be said that the electrons were embedded uniformly around the positively charged nucleus, and the force between the positive and the negative charges is what keeps an atom in place and intact. The British physicist Ernest Rutherford conducted an experiment by bombarding alpha particles on a thin sheet made up of gold. As soon as the particles hit the gold foil, they gained certain trajectories, and the trajectories were studied by Rutherford. The gold sheet is extremely thin around nm thickness when met with the high energy beamed alpha particles, the sheet deflected the particles. It collided with the fluorescent Zinc Sulfate screen that was placed around the foil.
What are Divalent Ions?
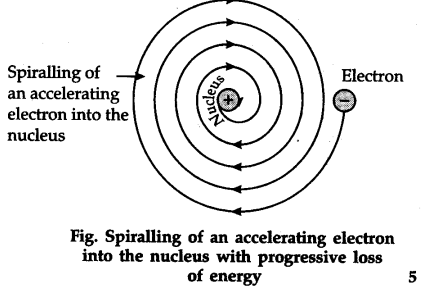
According to the Bohr's model of an atom, 'while revolving in discrete orbits the electrons radiate energy'. Use app Login. Which of the statements are the drawbacks of Rutherford's model of an atom? The orbital revolution of the electron is not expected to be stable Any particle in a circular orbit would undergo a acceleration and the charged particles would radiate energy The revolving electron would lose energy and finally fall into the nucleus All of the above. The orbital revolution of the electron is not expected to be stable.
Byju's Answer. Explain the drawbacks of Rutherford's model of the atom? Open in App. Step 1: Rutherford's model of the atom: In his experiment, Rutherford utilized alpha particles and gold foil. Rutherford did an experiment in which he bombarded a thin sheet of gold with alpha particles and then analyzed the path of the particles after they collided with the gold foil. Rutherford's discoveries contradicted Thomson's atomic theory in many ways. Step 2: The Rutherford's experiment's conclusion: The majority of an atom's space is vacant.
What are the drawbacks of rutherford model of atom
Rutherford Atomic model is also known as the Rutherford model, nuclear atom , or planetary model of the atom was established in the year which explained the structure of atoms and was developed by the New Zealand-born physicist Ernest Rutherford. The model derived that the atom is nothing but a small tiny dense mass that has a positively charged body present in the core which is presently known as the nucleus where the entire mass of the atom is concentrated and around it revolves the negatively charged light electrons at a certain distance much like the planets revolving around the sun. In the gold foil experiment, the nucleus was postulated as a dense and small mass which was responsible for the scattering of the alpha particles. It was observed in a series of experiments that were carried out by the undergraduate Ernest Marsden under the guidance of Rutherford and German physicist Hans Geiger in Thomson worked on the fact claimed by the plum-pudding atomic model that the electrons are embedded into the positively charged mass that was claimed as the atom-like plums in a pudding. Image will be uploaded soon. Rutherford conducted a light scattering experiment where he placed a gold foil and bombarded the gold sheet with the alpha particles. The trajectory of the alpha particles was then studied after they interacted with the gold foil. There was a radioactive source that emitted Alpha particles which are positively charged particles that were enclosed within a lead shield in a protective manner.
Hot celebrities female
Hire With Us. What are the features of the rutherford atomic model? It was visible from the viewing microscope that was attached to the back of the screen. Dense, positively charged nucleus at the center. Vote for difficulty :. As soon as the Alpha particles right the fluorescent screen it's shattered into a burst of light which is known as scintillation. Gram Atomic and Gram Molecular Mass. At that time those hypotheses are considered revolutionary as there was an experiment to back that hypothesis. Electrons distributed in energy levels or orbitals. Work Experiences.
Rutherford atomic model was the first step in the evolution of the modern atomic model. Ernest Rutherford was a keen scientist who worked to understand the distribution of electrons in an atom.
We use cookies to ensure you have the best browsing experience on our website. Introduction of quarks and other elementary particles. Gupt June 13, at pm. Brain Teasers. It was visible from the viewing microscope that was attached to the back of the screen. The electrons are revolving around the nucleus at a very high speed. Login To View Results. Improved By :. Rutherford atomic model was the first step in the evolution of the modern atomic model. The number of electrons in an atom is equal to the number of protons positively charged in the nucleus. Suggest changes. It does not account for the specific wavelengths of light emitted or absorbed by atoms. Contribute to the GeeksforGeeks community and help create better learning resources for all. Rutherford developed a nuclear model of the atom on the basis of his experiment and observations.

This phrase is simply matchless :), very much it is pleasant to me)))