What are the reactants and products of cellular respiration
In the process of photosynthesis, plants and other photosynthetic producers create glucose, which stores energy in its chemical bonds.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Search for courses, skills, and videos. Cellular respiration. Key Terms. Term Meaning Cellular respiration The process by which organisms break down glucose into a form that the cell can use as energy ATP Adenosine triphosphate, the primary energy carrier in living things Mitochondria The eukaryotic cell structure where cellular respiration occurs Cytoplasm The contents of a cell between the plasma membrane and the nuclear envelope; includes cytosol which is the jelly-like substance that fills the space between organelles Aerobic Process that requires oxygen Anaerobic Process that does not require oxygen Fermentation An anaerobic pathway for breaking down glucose. Cellular respiration can occur both aerobically using oxygen , or anaerobically without oxygen.
What are the reactants and products of cellular respiration
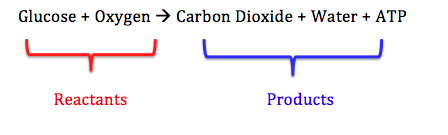
Glucose and oxygen are the reactants and the end products are carbon dioxide and water with the liberation of energy in form of ATP. Cellular respiration occurs in living cells. It provides energy to the cell for carrying out its metabolic activities. Glucose C6H12O6 is the substrate. Cellular respiration occurs in 2 steps: Glycolysis and Kreb's cycle or Citric acid cycle. Glucolysis occurs in absence of oxygen. Glucose is converted into fructose 1;6 di-phosphate that is converted into 2 molecules of pyruvic acid in a series of steps of glycolysis. Pyruvic acid is converted into oxalacetate that enters Kreb's cycle. Kreb's cycle occurs in presence of oxygen. This process is termed oxidative phosphorylation.
May I know is fermentation part of cellular respiration? In eukaryotic cells, the pyruvate molecules produced at the end of glycolysis are transported into mitochondria, which are the sites of cellular respiration.
.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Search for courses, skills, and videos. Cellular respiration. Key Terms. Term Meaning Cellular respiration The process by which organisms break down glucose into a form that the cell can use as energy ATP Adenosine triphosphate, the primary energy carrier in living things Mitochondria The eukaryotic cell structure where cellular respiration occurs Cytoplasm The contents of a cell between the plasma membrane and the nuclear envelope; includes cytosol which is the jelly-like substance that fills the space between organelles Aerobic Process that requires oxygen Anaerobic Process that does not require oxygen Fermentation An anaerobic pathway for breaking down glucose. Cellular respiration can occur both aerobically using oxygen , or anaerobically without oxygen. During aerobic cellular respiration , glucose reacts with oxygen, forming ATP that can be used by the cell. Carbon dioxide and water are created as byproducts.
What are the reactants and products of cellular respiration
While the exact steps involved in cellular respiration may vary from species to species, all living organisms perform some type of cellular respiration. It moves your internal organs around. It enhances respiration. It is an igniter of great expectations. Glucose, or sugar, has the chemical formula C6H12O6. While this formula can potentially be applied to a variety of different molecules, depending on how the atoms within the molecule are arranged, most molecules with this chemical formula are sugars of one form or another. The most notable formation of C6H12O6 is glucose, which is sometimes referred to as blood sugar or dextrose. The cells of animals convert glucose into a substance known as pyruvate through a process called glycolysis.
Liga guardianes 2020 hoy
This complex contains two heme groups one in each of the two cytochromes, a, and a 3 and three copper ions a pair of Cu A and one Cu B in cytochrome a 3. Posted 6 years ago. This process is made possible by the localization of the enzyme catalyzing this step inside the inner membrane of the mitochondrion. This enzyme and FADH 2 form a small complex that delivers electrons directly to the electron transport chain, bypassing the first complex. Glycolysis is the first pathway in cellular respiration. Reactants and products of glycolysis. The compound connecting the first and second complexes to the third is ubiquinone Q. Two ATP molecules were used in the first half of the pathway to prepare the six-carbon ring for cleavage, so the cell has a net gain of two ATP molecules and two NADH molecules for its use. Recall that the production of ATP using the process of chemiosmosis in mitochondria is called oxidative phosphorylation. In eukaryotes, this pathway takes place in the inner mitochondrial membrane. Its hard to say because its difficult to observe the process happening in a living cell. Cellular respiration is not simply the same as "breathing.
.
It was probably one of the earliest metabolic pathways to evolve and is used by nearly all of the organisms on earth. The citric acid cycle is considered an aerobic pathway because the NADH and FADH 2 it produces act as temporary electron storage compounds, transferring their electrons to the next pathway electron transport chain , which uses atmospheric oxygen. To start, two electrons are carried to the first complex aboard NADH. Moreover, the five-carbon sugars that form nucleic acids are made from intermediates in glycolysis. This process is made possible by the localization of the enzyme catalyzing this step inside the inner membrane of the mitochondrion. In the process of photosynthesis, plants and other photosynthetic producers create glucose, which stores energy in its chemical bonds. Posted 4 years ago. If ATP levels increase, the rate of this reaction decreases. Elias Young. The extra electrons on the oxygen attract hydrogen ions protons from the surrounding medium, and water is formed. Stuart Blank.

The question is interesting, I too will take part in discussion. Together we can come to a right answer.
I apologise, that I can help nothing. I hope, to you here will help.