What is kranz anatomy class 11
Question 41 In what kind of plants do you come across 'Kranz anatomy'? To which conditions are those plants better adapted? How are these plants better adapted than the plants, which lack this anatomy?
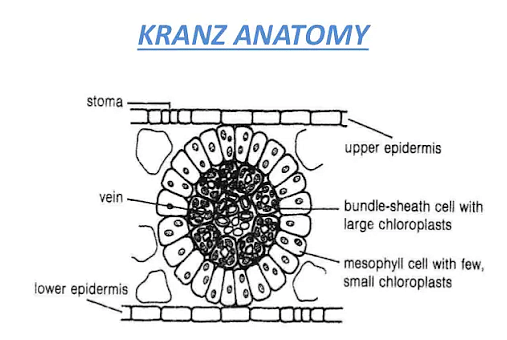
Kranz Anatomy is one structure within the leaves of the C4 plants that are specialized in nature. This is where the spongy mesophyll cells are found bundled up. They are seen in a ring-like shape that surrounds the veins of a leaf. Kranz anatomy is a unique structure observed in C4 plants. Also, the number of chloroplasts observed in bundle sheath cells is more than that in the mesophyll cell. This entire structure is densely packed and plays a major role in C4 photosynthesis. We have established with the help of the above definitions that Kranz Anatomy is a significant part of C4 plants.
What is kranz anatomy class 11
In this article, we have discussed the kranz anatomy. We have also discussed the examples and the diagram of Kranz anatomy. The mainly large cells surrounding the vascular bundles of the C4 plants are termed bundle sheath cells and the leaves which have such structure are said to have Kranz anatomy. Kranz means wreath and shows the preparation of cells. The bundle sheath cells may create several sheets around the vascular bundles that are categorized by numerous chloroplasts, impenetrable walls for gaseous exchange, and no intercellular spaces. For example, such anatomy is well-observed in maize. In the common of plants, together with rice, carbon dioxide is first made static into a compound with three carbons atoms C3 by the photosynthetic enzyme- ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase oxygenase or simply Rubisco. This is known as C3 photosynthesis. Rubisco is integrally unproductive because it can also catalyze a reaction with oxygen, giving an inefficient method known as photorespiration rather than photosynthesis. To wave off this incompetence, the C4 path primarily fixes carbon dioxide in the atmosphere into C4 acids using the enzyme phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase which is unresponsive to oxygen. Next, C4 acids release carbon dioxide for re-fixation by Rubisco. In many C4 plants, these two phases of the C4 trail are spatially divided into morphologically different photosynthetic cell categories, allowing a high concentration of carbon dioxide to gather in the area of Rubisco, and better photosynthetic productivity. In C4 grasses such as maize and some C4 dicots, distended bundle sheath BS cells border the veins V and the BS cells are then enclosed by mesophyll M cells. An entirely efficient C4 trail, therefore, requires a synchronized alteration in the structure of the tissue and metabolic biochemistry. During development, these variations have happened more than fifty times in an extensive range of blooming plants, representing that, even with being critical, it is a comparatively easy trail to progress.
As a result, the plant is able to produce more sugar and oxygen for utilisation by the plant. But how are they different? Ans: C3 plants and C
Kranz anatomy is a specialized structure in C 4 Plants where the mesophyll cells are clustered around the bundle-sheath cells in a ring-like fashion. The number of chloroplasts in the bundle-sheath cells is more than that in the mesophyll cells. This is found in C 4 grasses such as maize and a few dicots. The Kranz anatomy is developed in three different steps:. Also read: Photosynthesis in Higher Plants.
Kranz Anatomy is one structure within the leaves of the C4 plants that are specialized in nature. This is where the spongy mesophyll cells are found bundled up. They are seen in a ring-like shape that surrounds the veins of a leaf. Kranz anatomy is a unique structure observed in C4 plants. Also, the number of chloroplasts observed in bundle sheath cells is more than that in the mesophyll cell. This entire structure is densely packed and plays a major role in C4 photosynthesis.
What is kranz anatomy class 11
Kranz anatomy is a unique feature of C 4 plants where the mesophyll cells form a circular pattern around the bundle-sheath cells. This structure is named after the German word 'Kranz' which translates to 'wreath' or 'ring'. It's commonly observed in C 4 grasses like maize and some dicotyledonous plants.
What episode does jinbei join the crew
FREE Signup. In C4 plants, the growth occurs when the soil temperature is between degrees. Based on Photosynthesis: C3 completes photosynthesis only when stomata are open. View Solution. To get rid of this, the C4 pathway uses the enzyme phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase to fix atmospheric carbon dioxide. Yes, you are correct. Mesophyll cells are homogenous and organized in concentric sheets around the vascular bundles. Related articles. Bundle sheath cells are thick-walled tubular cells. So the C4 plants have to minimise the water loss in hot and dry environments. All the C4 Plants possess the dimorphic chloroplasts. Are you a Sri Chaitanya student? The main differences between the C3 and C4 plants are that the bundle sheath cells of C3 plants do not contain chloroplast whereas the bundle sheath cells of C4 plants do. Also, the number of chloroplasts observed in bundle sheath cells is more than that in the mesophyll cell. Fig: Plasmodesmata Dimorphic chloroplast Bundle sheath cells and mesophyll cells have chloroplast present in them.
Kranz Anatomy is a distinctive arrangement found in C4 plants, characterized by mesophyll cells forming a ring around the bundle-sheath cells.
These many adaptations are there for a plant to live and survive in a particular environment. One is that these plants are able to produce more biomass than plants with alternative leaf structures. The agranal chloroplast is present in bundle-sheath cells. Skip to main navigation. Skip to content Search for:. Also, the number of chloroplasts observed in bundle sheath cells is more than that in the mesophyll cell. Many well-developed and large grana are present. Some plants show resistance to root rot. This is known as C3 photosynthesis. RuBP carboxylase is absent. So what makes these C4 plants special than the C3 plants? Mesophyll cells are homogenous and organized in concentric sheets around the vascular bundles. Ans: C 3 plants are those plants that practice the Calvin cycle for the dark reaction of photosynthesis.

0 thoughts on “What is kranz anatomy class 11”