What is pulmonary surfactant
Pulmonary surfactant is a complex and highly surface active material composed of lipids and proteins which is found in the fluid lining the alveolar surface of the lungs.
Surfactant is an agent that decreases the surface tension between two media. The surface tension between gaseous-aqueous interphase in the lungs is decreased by the presence of a thin layer of fluid known as pulmonary surfactant. It is essential for efficient exchange of gases and for maintaining the structural integrity of alveoli. Surfactant is a secretory product, composed of lipids and proteins. The lipid and protein components are synthesized separately and are packaged into the lamellar bodies in the AT-II cells.
What is pulmonary surfactant
Pulmonary surfactant is a surface-active complex of phospholipids and proteins formed by type II alveolar cells. By adsorbing to the air-water interface of alveoli , with hydrophilic head groups in the water and the hydrophobic tails facing towards the air, the main lipid component of surfactant, dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine DPPC , reduces surface tension. As a medication, pulmonary surfactant is on the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines , the most important medications needed in a basic health system. Alveoli can be compared to gas in water, as the alveoli are wet and surround a central air space. The surface tension acts at the air-water interface and tends to make the bubble smaller by decreasing the surface area of the interface. Compliance is the ability of lungs and thorax to expand. Lung compliance is defined as the volume change per unit of pressure change across the lung. This difference in inflation and deflation volumes at a given pressure is called hysteresis and is due to the air-water surface tension that occurs at the beginning of inflation. However, surfactant decreases the alveolar surface tension , as seen in cases of premature infants with infant respiratory distress syndrome. Pulmonary surfactant thus greatly reduces surface tension , increasing compliance allowing the lung to inflate much more easily, thereby reducing the work of breathing. It reduces the pressure difference needed to allow the lung to inflate. The lung's compliance, and ventilation decrease when lung tissue becomes diseased and fibrotic. As the alveoli increase in size, the surfactant becomes more spread out over the surface of the liquid. This increases surface tension effectively slowing the rate of expansion of the alveoli.
ISBN
.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Hina Khawar ; Komal Marwaha. Authors Hina Khawar ; Komal Marwaha 1. Pulmonary surfactant is a lipoprotein complex that lines the alveoli and decreases the surface tension to prevent lung atelectasis. Surfactant deficiency is a documented cause of neonatal respiratory distress syndrome NRDS , a significant cause of morbidity and mortality in premature infants. Therapeutic indications for surfactant replacement therapy include neonates with clinical and radiographic evidence of respiratory distress syndrome RDS and infants who require endotracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation secondary to respiratory failure. Surfactant is prophylactically administered in neonates at risk of developing NRDS.
What is pulmonary surfactant
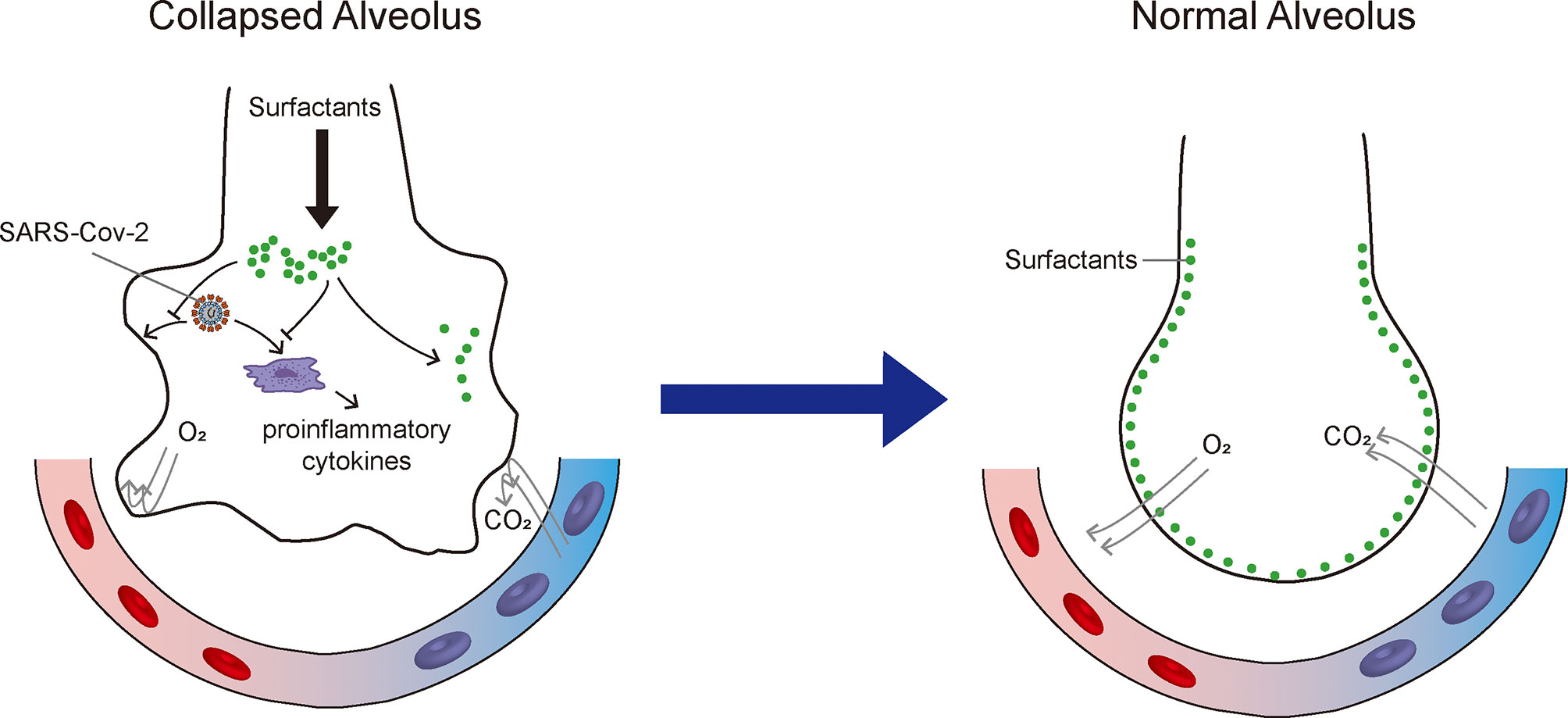
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Pulmonary surfactant is essential for life as it lines the alveoli to lower surface tension, thereby preventing atelectasis during breathing. The hydrophobic proteins, SP-B and SP-C, together with dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine, confer surface tension—lowering properties to the material. The more hydrophilic surfactant components, SP-A and SP-D, participate in pulmonary host defense and modify immune responses. Specifically, SP-A and SP-D bind and partake in the clearance of a variety of bacterial, fungal, and viral pathogens and can dampen antigen-induced immune function of effector cells. Emerging data also show immunosuppressive actions of some surfactant-associated lipids, such as phosphatidylglycerol.
Mdw2 joliet il
The DPPC is the strongest surfactant molecule in the pulmonary surfactant mixture. Alveolar surfactant has a half-life of 5 to 10 hours once secreted. Philadelphia, PA. Changes in the surfactant mixture composition alter the pressure and temperature conditions for phase changes and the phospholipids' crystal shape as well. Ex-situ measurements of surface tension and interfacial rheology can help to understand the functionality of pulmonary surfactants. They undergo much post-translational modification, ending up in the lamellar bodies. Publication types Research Support, Non-U. Retrieved Even though the surface tension can be greatly reduced by pulmonary surfactant, this effect will depend on the surfactant's concentration on the interface. Lamellar bodies appear in the cytoplasm at about 20 weeks gestation.
Pulmonary surfactant is a surface-active complex of phospholipids and proteins formed by type II alveolar cells.
Toggle limited content width. Therefore, the surface tension varies according to the volume of air in the lungs, which protects them from atelectasis at low volumes and tissue damage at high volume levels. Ch Lamellar bodies appear in the cytoplasm at about 20 weeks gestation. Wheater's functional histology : a text and colour atlas. Nevertheless, it has been observed that if a lung region is abruptly expanded the floating crystals crack like " icebergs ". Molecular Genetics and Metabolism. Archived from the original on PMID It reduces the pressure difference needed to allow the lung to inflate. In late s von Neergaard [22] identified the function of the pulmonary surfactant in increasing the compliance of the lungs by reducing surface tension. It also has a higher compaction capacity than the other phospholipids, because the apolar tail is less bent. Annals of Anatomy. Alterations in surfactant homeostasis or biophysical properties can result in surfactant insufficiency which may be responsible for diseases like respiratory distress syndrome, lung proteinosis, interstitial lung diseases and chronic lung diseases. Categories : Respiratory physiology Integral membrane proteins Surfactants Pulmonary function testing Lipopeptides.

Likely is not present
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are not right. Let's discuss it. Write to me in PM.
The amusing information