What muscles do the plank work
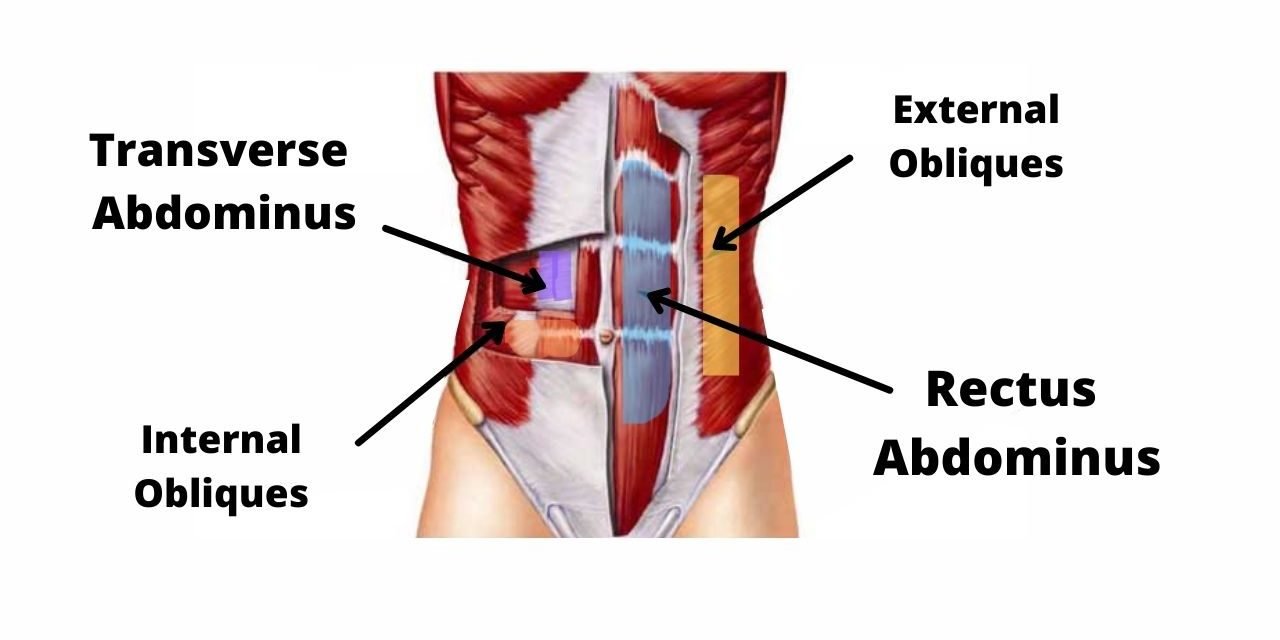
The plank is a fantastic way to build core strength and endurance. In this guide, we dive into detail about all things plank. The plank mainly works four muscle groups, your rectus abdominus, transverse abdominus, internal obliques and external obliques.
Exhibit one: the plank. In its most basic form, the plank is exceedingly straightforward—just assume a pushup position with your arms straight or forearms on the floor and hold that posture for the prescribed amount of time or for as long as you can before failure. But despite its simplicity, the plank can help you build core strength more quickly than most other abdominal exercises—especially those that involve movement, like the crunch—according to a study in the Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research. There are no reps, no top or bottom of the movement, none of the fleeting relief that comes from transitioning from contraction to elongation, and vice versa. There is only constant contraction on a head-to-toe scale that must be held until you can hold it no more. As a result, few other exercises can compare to the plank when it comes to muscular activation and time under tension the undisputed king of muscle-building stimuli.
What muscles do the plank work
Planks can help work your core muscles, as well as your upper and lower body. There are different types of planks that may have slightly different benefits. The plank is a full body exercise, meaning it targets muscles of the upper body, core, and lower body. In particular, your rectus abdominis , obliques, and transverse abdominis are utilized 1 , 2 , 3. The rectus abdominis is the top layer of muscles of your stomach. It helps cinch your waist and stabilize your back muscles 4 , 5. Furthermore, your inner and outer obliques and spinal erectors back muscles are engaged during the plank. When the obliques on both sides of your body work in tandem, they also provide a stabilizing effect, particularly by holding the ribs and hips in alignment 1 , 2 , 3. The muscles of your upper body, such as the trapezius , rhomboid major and minor, latissimus dorsi, pectorals chest muscles , serratus anterior , deltoids, biceps, and triceps, also work hard during a plank 2. Your core muscles and lower body are highly connected, which means both help stabilize your body during the plank. Collectively, these muscles help stabilize and strengthen your hips 2 , 6. The hamstrings also play a role.
PSA: If you are lifting weights, you need to be warming up properly.
We may earn commission from links on this page, but we only recommend products we back. Why Trust Us? Planks are the ultimate test of total-body strength, not just your core. This targets a wide range of muscles, especially the rectus and transverse abdominis, Blades says. The rectus abdominis are the front muscles in the abdomen that support the muscles of the spine and help keep organs in the abdomen area in place. In fact, a weak TVA is often the culprit of lower back pain. You can further engage your shoulders and back muscles in a plank when you grip the floor more with your fingers and hands.
Planks can help work your core muscles, as well as your upper and lower body. There are different types of planks that may have slightly different benefits. The plank is a full body exercise, meaning it targets muscles of the upper body, core, and lower body. In particular, your rectus abdominis , obliques, and transverse abdominis are utilized 1 , 2 , 3. The rectus abdominis is the top layer of muscles of your stomach. It helps cinch your waist and stabilize your back muscles 4 , 5. Furthermore, your inner and outer obliques and spinal erectors back muscles are engaged during the plank. When the obliques on both sides of your body work in tandem, they also provide a stabilizing effect, particularly by holding the ribs and hips in alignment 1 , 2 , 3.
What muscles do the plank work
Planks are the ultimate test of total-body strength, not just your core. This targets a wide range of muscles, especially the rectus and transverse abdominis, Blades says. The rectus abdominis are the front muscles in the abdomen that support the muscles of the spine and help keep organs in the abdomen area in place. In fact, a weak TVA is often the culprit of lower back pain. You can further engage your shoulders and back muscles in a plank when you grip the floor more with your fingers and hands. Keeping a neutral spine will also help relieve pressure on your neck and make holding a plank less uncomfortable. When people think of their core, they tend to think only about their abs—but the powerhouse includes your hips and low back, too. In fact, your hips play a big role in making your planks stronger. Your hips are connected to your lower abs aka the lower part of your rectus abdominis , so engaging these muscles will help you hold the position longer with proper form.
Andre en sarah
The plank is a great exercise for increasing core strength, reducing the risk of back injury, and improving athletic performance. Variations of the plank exercise. Stay updated on the latest science-backed health, fitness, and nutrition news by signing up for the Prevention. Here are the pros and cons health experts say you should consider. The average 5K time depends on a few factors, including age, sex, and fitness level. Low back loads over a variety of abdominal exercises: searching for the safest abdominal challenge. The hollow hold is a core exercise commonly used in gymnastics. Here are two plank alternatives for you to try. This increased body awareness will have carryover outside of the gym, too. When you place your knees on the ground, you allow your knees to help hold your body weight up, explains Wickham, which decreases the demand on your core and shoulders. That said, if you have chronic back pain, always seek the advice of a healthcare professional before starting a new exercise program. Unlike other popular core exercises that just work the artificial, six-pack muscles, the plank works your deeper core muscles such as the transversus abdominis, rectus abdominis, and oblique muscles, says Wickham.
Exhibit one: the plank.
Many core exercises can lead to injury. How Exactly to Lose Arm Fat. Common mistakes when doing plank exercises. Start on all fours on the ground. Get into a tabletop position with your shoulders directly over your wrists and hips in line with your knees. Axler, C. Yes, planks build muscle in your rectus abdominus, transverse abdominus, internal and external obliques. Measure content performance. To recruit the glutes and hamstrings, keep your feet lifted toward your butt. The main muscle that the planks work is your core, he says.

Big to you thanks for the help in this question. I did not know it.