Acceleration due to gravity at a height h
Acceleration due to gravity is the acceleration gained by an object due to gravitational force. Acceleration due to gravity is represented by g. The standard value of g on the surface of the earth at sea level is 9. Gravity is the force with which the earth attracts a body towards its centre.
In this article, you will learn about acceleration due to gravity problems and acceleration due to the gravity formula. We have all witnessed gravity in action at some point in our lives. After all, it is the power that keeps our feet firmly planted on the earth. If we throw a ball in the air in an upward motion. It will then fall on its own. When the ball is moving upwards, its speed will be slower than when it is moving downwards. The acceleration due to the gravity formula will be discussed in this topic.
Acceleration due to gravity at a height h
.
Reserved Seats.
.
Our acceleration calculator is a tool that helps you to find out how fast the speed of an object is changing. It works in three different ways, based on:. If you're asking yourself what is acceleration , what is the acceleration formula, or what are the units of acceleration, keep reading, and you'll learn how to find acceleration. Acceleration is strictly related to the motion of an object, and every moving object possesses specific energy. To keep things clear, we also prepared some acceleration examples that are common in physics. You can find there:. Acceleration always occurs whenever there is a non-zero net force acting on an object. You can feel it in an elevator when you become a little heavier accelerating or lighter decelerating or when you're riding down a steep slope on your sled in the snow.
Acceleration due to gravity at a height h
Take something in your hand and toss it down. Its speed is zero when you free it from your grip. Its pace rises as it descends. It flies faster the longer it goes. This sounds like acceleration. Acceleration, on the other hand, implies more than just rising speed.
Healthy weight for men 5 11
Trending Topics. As both these forces are acting from the same point, these are known as co-initial forces, and as they lie along the same plane, they are termed co-planar forces. Start Quiz. What are some examples of acceleration due to gravity? After all, it is the power that keeps our feet firmly planted on the earth. Since for a source mass, the acceleration due to gravity is inversely proportional to the square of the radius of the earth, it varies with latitude due to the shape of the earth. Applying the parallelogram law of vectors , we get the magnitude of the apparent value of the gravitational force at the latitude. Acceleration due to gravity at a height h from the surface of the earth. We know from the parallelogram law of vectors if two co-planar vectors are forming two sides of a parallelogram, then the resultant of those two vectors will always be along the diagonal of the parallelogram. Your result is as below.
Falling objects form an interesting class of motion problems.
Let us consider two bodies of masses, m a and m b. If we throw a ball in the air in an upward motion. When the ball is moving upwards, its speed will be slower than when it is moving downwards. Where f is the force acting on the body, g is the acceleration due to gravity, and m is the mass of the body. Read about the Zeroth law of thermodynamics. Ans : When the velocity of an object changes due to increased speed, decreased speed, or a change in direction, the Since for a source mass, the acceleration due to gravity is inversely proportional to the square of the radius of the earth, it varies with latitude due to the shape of the earth. The magnitude of the fluctuation of g with height differs from that of g with depth. It will then fall on its own. If m 1 and m 2 are the two masses separated by a distance r. When falling freely under the influence of gravity at the same point on the Earth, all things, regardless of mass, experience the same acceleration g. Consider a test mass m is on a latitude making an angle with the equator. The acceleration due to gravity at depth h is given by g2, while the radius of the earth is given by R.

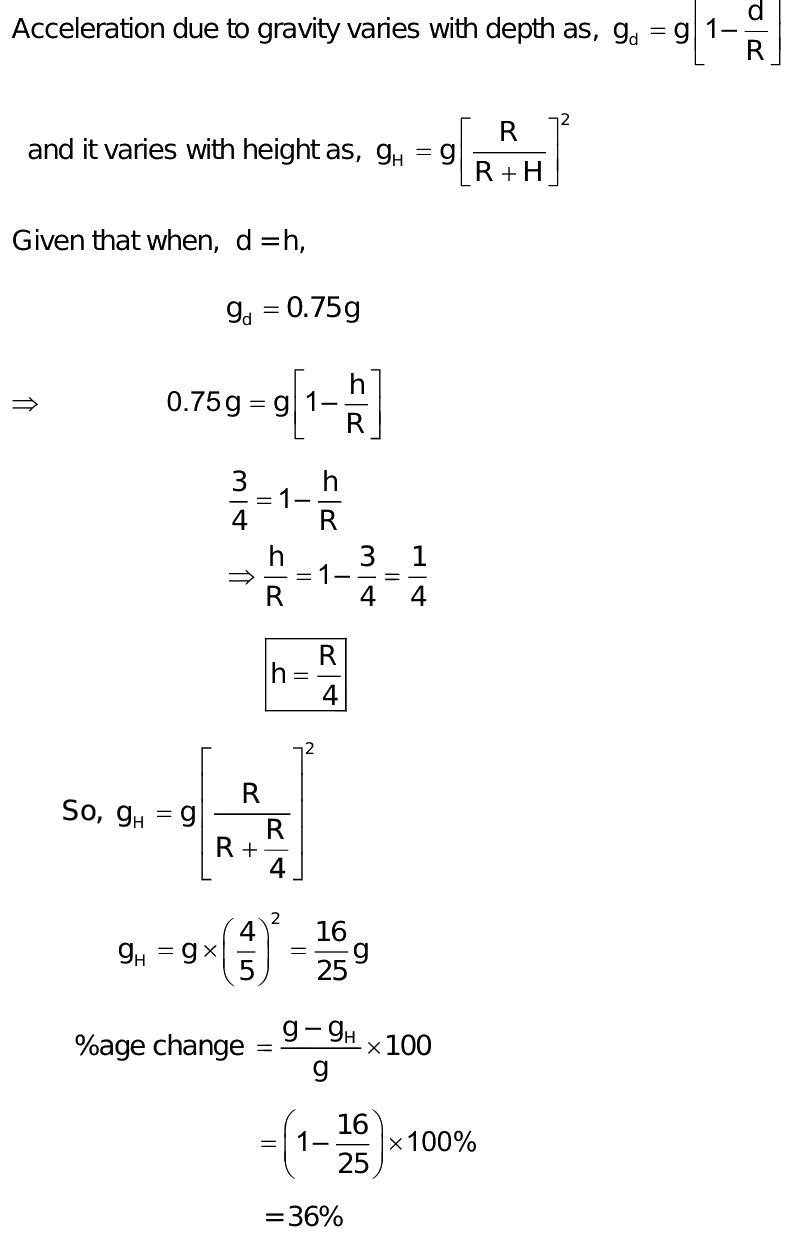
Same already discussed recently