Acetic acid lewis dot structure
Weekly Web Work 7: a.
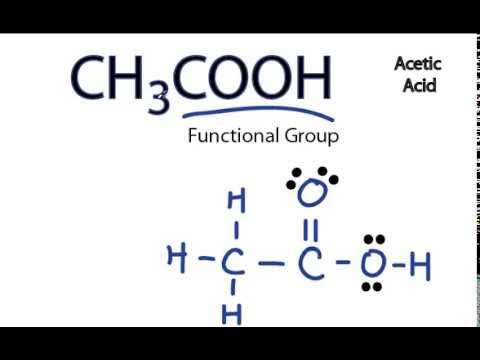
Lewis Dot Structures. This assignment is past due and can no longer be submitted. The purpose of this assignment is to practice drawing Lewis dot structures. You will need to have a pencil and paper to use while working on this assignment. In order to draw the Lewis structure of acetic acid, you need to determine the number of valence electrons. Carbon has 4, oxygen has 6, and hydrogen has 1 valence electron.
Acetic acid lewis dot structure
.
You will need to have a pencil and paper to use while working on this assignment.
.
It corrodes both metals and tissues. Long-term acetic acid exposure can cause serious irritation in the eyes, skin, nose, throat, and other body parts, among other things. When acetic acid reaches 40 degrees Celsius, it becomes flammable and explosive. In its liquid state, acetic acid is a polar or protic solvent. Lewis structure , also known as electron dot structure, aids in understanding how atoms or valence electrons are grouped in a molecule. As a result, the first step in constructing a Lewis diagram for every molecule is to figure out how many valence electrons are present. Because carbon is in the 14th periodic group, oxygen is in the 16th, and hydrogen is in the first group of the periodic table, As a result, the valence electron for carbon is 4, the valence electron for oxygen is 6, and the valence electron for hydrogen is 1. This is due to the fact that at their outermost shells, hydrogen can only retain two valence electrons. Because the carbon atom has a lower electronegative charge than the oxygen atom, it occupies the middle position in the Lewis diagram.
Acetic acid lewis dot structure
We begin our discussion of the relationship between structure and bonding in covalent compounds by describing the interaction between two identical neutral atoms—for example, the H 2 molecule, which contains a purely covalent bond. Each hydrogen atom in H 2 contains one electron and one proton, with the electron attracted to the proton by electrostatic forces. As the two hydrogen atoms are brought together, additional interactions must be considered Figure 5. Figure 5. Electron—electron and proton—proton interactions are repulsive; electron—proton interactions are attractive. At the observed bond distance, the repulsive and attractive interactions are balanced. A plot of the potential energy of the system as a function of the internuclear distance Figure 5. Thus at intermediate distances, proton—electron attractive interactions dominate, but as the distance becomes very short, electron—electron and proton—proton repulsive interactions cause the energy of the system to increase rapidly.
Airfare san jose to las vegas
Describe your Lewis dot structure. Does the total number of electrons in your Lewis structure match the number of valence electrons actually available? How is your structure for CS 2 similar to your structure for CO 2? If not, you need to add lone pairs to satisfy each atom. First, determine the number of valence electrons. Chloroform, CHCl 3 , was an early anesthetic. Lecture Audio. Chloroform, CHCl 3 , was an early anesthetic. How many single bonds does chloroform have? Our Chemical World. How many valence electrons does carbon disulfide have?
In this comprehensive guide, we will take you through the process of drawing the Lewis structure for CH3COOH, also known as acetic acid, a molecule with significant importance in organic chemistry and beyond. Find the Total Valence Electrons.
The purpose of this assignment is to practice drawing Lewis dot structures. Absence Excuse Form. Our Chemical World. If yes, cool. How many valence electrons does carbon disulfide have? Our Chemical World. Look at the Lewis structure of acetic acid. How many double bonds? How many single bonds does chloroform have? Look at the structure on the left.

Very good piece
I join told all above. Let's discuss this question.