Acinus pancreas
Acinar cell carcinoma of the pancreasacinus pancreas, also acinar cell carcinomais a rare malignant exocrine tumour of the pancreas.
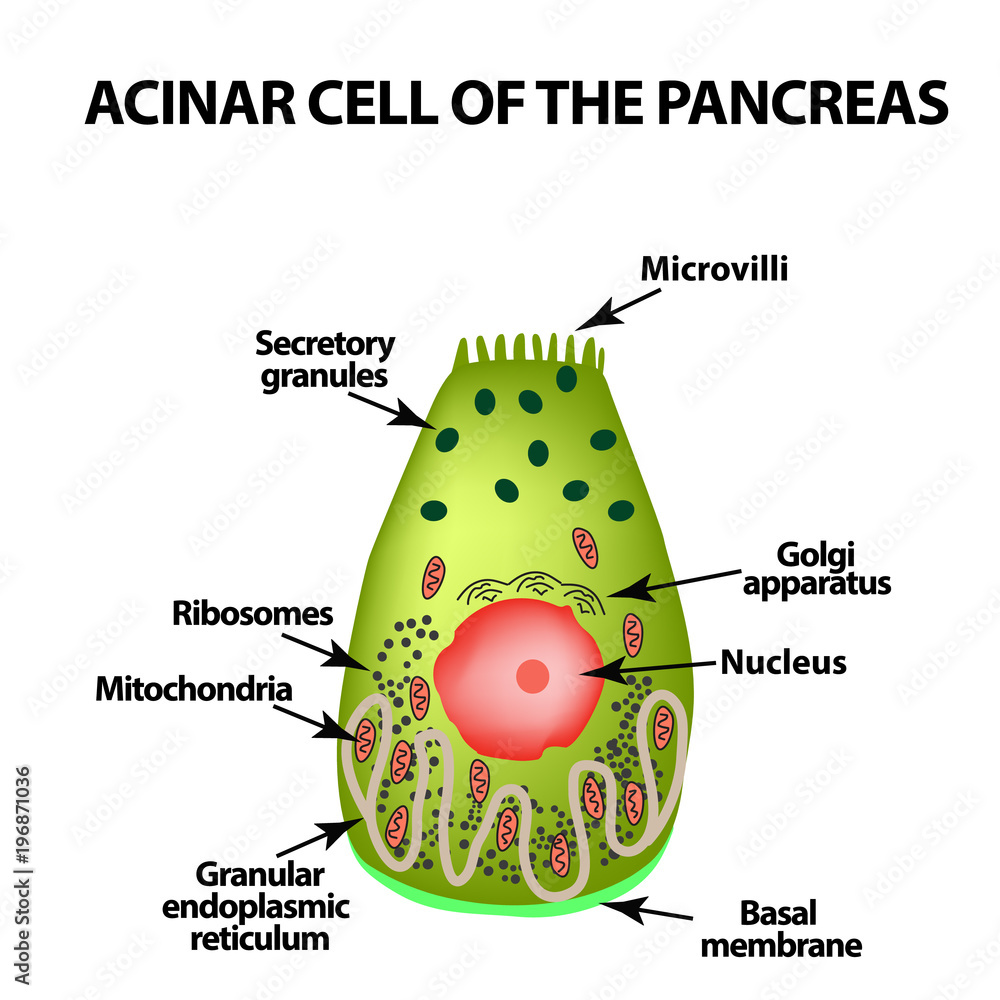
The pancreatic acinar cell is the functional unit of the exocrine pancreas. It synthesizes, stores, and secretes digestive enzymes. Under normal physiological conditions, digestive enzymes are activated only once they have reached the duodenum. Premature activation of these enzymes within pancreatic acinar cells leads to the onset of acute pancreatitis; it is the major clinical disorder associated with pancreatic acinar cells. Although there have been major advances in our understanding of the pathogenesis of this disease in recent years, available treatment options are still limited to traditional nonspecific and palliative interventions.
Acinus pancreas
Acini and Centro-acinar Cells. The exocrine pancreas is a compound gland consisting of secretory endpieces acini draining into a converging duct system [5,17,30]. The acini, which are composed of cells that synthesise digestive enzymes and store them as zymogen granules, are found at the terminations of the intercalated ducts, but also, in some species, at intermediate points along the ducts, so that an acinus may surround an intercalated duct part way along its course. In most species, the individual cells form truncated pyramids so that, when they are aggregated to form a secretory endpiece, the endpiece is shaped like a berry Latin: acinus rather than being tubular [64]. Each acinus envelops a layer of intercalated duct cells which, in consequence, are often called centro-acinar cells, although there is no evidence to suggest that they differ morphologically or functionally from cells elsewhere in the intercalated ducts. These keywords were added by machine and not by the authors. This process is experimental and the keywords may be updated as the learning algorithm improves. This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution. Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF. In: Johnson LR ed Physiology of the gastrointestinal tract, vol 2, 3rd edn. Raven, New York, pp — Google Scholar.
Korean J Gastroenterol.
A pancreatic acinus is a functional unit of the exocrine pancreas producing digest enzymes. Its pathobiology is crucial to pancreatic diseases including pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer, which can initiate from pancreatic acini. However, research on pancreatic acini has been significantly hampered due to the difficulty of culturing normal acinar cells in vitro. In this study, an in vitro model of the normal acinus, named pancreatic acinus-on-chip PAC , is developed using reprogrammed pancreatic cancer cells. In this model, human pancreatic cancer cells, Panc-1, reprogrammed to revert to the normal state upon induction of PTF1a gene expression, are cultured. Bioinformatic analyses suggest that, upon induced PTF1a expression, Panc-1 cells transition into a more normal and differentiated acinar phenotype.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October Learn More or Try it out now. This review focuses on studies from the past year that have greatly advanced our understanding of molecular and cellular regulation of pancreatic acinar cell function. Recent advances focus on signals dictating pancreatic development, acinar cell fate, pancreatic growth, and secretion. Regeneration of acinar cells after pancreatitis depends on expression of embryonic signals in mature acinar cells. In this setting, acinar cells can also transdifferentiate into adipose cells.
Acinus pancreas
The pancreas is an abdominal organ located deep in the retroperitoneum. It is a gland with mixed function: both exocrine and endocrine. In this article, we will consider just the exocrine functions of the pancreas, the synthesis of pancreatic enzymes and the regulation of enzyme secretion. Finally, we will consider the clinical relevance of the pancreatic exocrine functions. When we consider the functions of the pancreas, it is simpler to view it as a mix of two glands. We can divide the pancreas into an exocrine gland, containing the acinar and duct tissue, and the endocrine gland containing the islets of Langerhans. The bicarbonate helps in neutralising the stomach acid.
Calibre 50 canciones
Conclusions We have created a new microfluidic model of a pancreatic acinus which presents many advantages over existing models. Cancer Biol , , 20 , — Micrograph of an acinar cell carcinoma of the pancreas. Paraffin was removed from the slices and treated with an antigen unmasking solution Vector Laboratories, CA. A , , , — This will create a duct structure, as reported previously. These cancer-associated properties are EMT-related pathways, cancer stemness, and drug resistance. Time-lapsed micrographs of duct and acinus sac formation are shown in Fig. Histomorphologically, the tumour resembles the cells of the pancreatic acini and, typically, have moderate granular cytoplasm that stain with both PAS and PASD. Without PTF1a induction, only small granules i. Feb This is confirmed by microscopic observation of drastic changes in the invasiveness of cancer cells after inducing PTF1a expression, and recovery of normal functionality of digestive enzyme production.
The pancreas is surrounded by a very thin connective tissue capsule that invaginates into the gland to form septae, which serve as scaffolding for large blood vessels. The large spaces between lobules seen in this image are a commonly-observed artifact of fixation. The exocrine pancreas is classified as a compound tubuloacinous gland.
Toggle limited content width. Raven, New York, pp — If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given. Authors D. Without Dox treatment, degradation of the matrix and local invasion of cells noted with arrows are observed. Gen Comp Endocrinol — After the microfabrication, the chip is first filled with a type I collagen solution Corning, NY. Development — In the Dox treatment group, zymogen granules noted with solid arrows are produced and localized near the apical side. Hruban, eds. Its pathobiology is crucial to pancreatic diseases including pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer, which can initiate from pancreatic acini. Wikimedia Commons. Cell Biol , , 20 , 69— Many advantages exist with the present platform over existing models.

Interesting variant