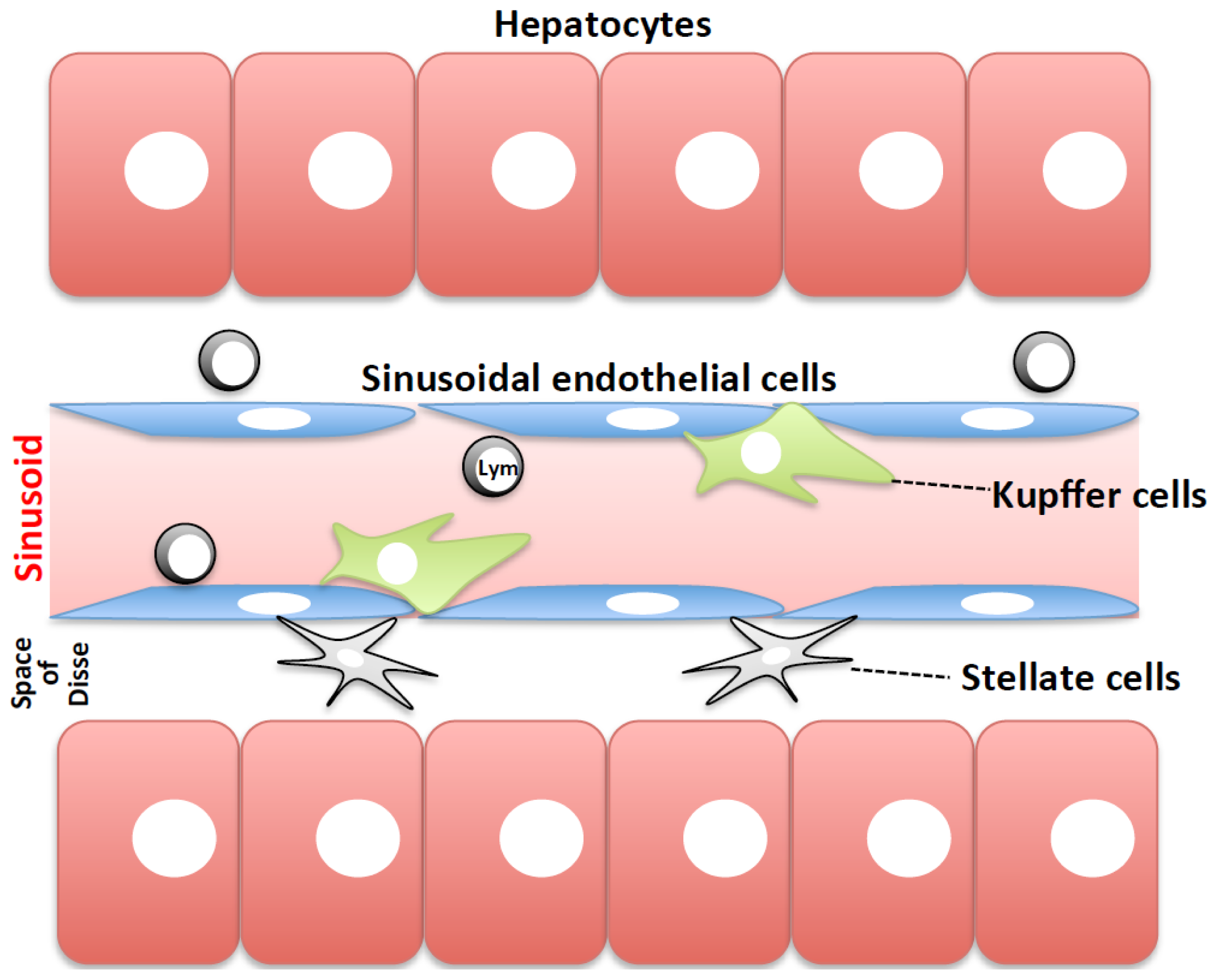
Kupfer cells
Aims: Kupffer cells KCs are the liver-resident macrophages and play a leading role in the regulation of liver homeostasis in physiological conditions and in pathology, kupfer cells. The study aims to investigate the anti-echinococcosis effect of KCs and the effects of hepatic stellate cells HSCs activation in the progression of liver fibrosis in hepatic alveolar echinococcosis hepatic AE. It is worth noticing that the expression levels of anti-inflammatory cytokines were kupfer cells higher than that of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Conclusions: Our research indicates that KCs have immune-protective effect of anti-echinococcosis and promote liver fiber repair, kupfer cells, and it also suggests that they have potential therapeutic value for patients with hepatic AE.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Kupffer cells are resident liver macrophages and play a critical role in maintaining liver functions. Under physiological conditions, they are the first innate immune cells and protect the liver from bacterial infections. Under pathological conditions, they are activated by different components and can differentiate into M1-like classical or M2-like alternative macrophages.
Kupfer cells
AoH publishes editorials, opinions, concise reviews, original articles, brief reports, letters to the editor, news from affiliated associations, clinical practice guidelines and summaries of congresses in the field of Hepatology. Our journal seeks to publish articles on basic clinical care and translational research focused on preventing rather than treating the complications of end-stage liver disease. The Impact Factor measures the average number of citations received in a particular year by papers published in the journal during the two preceding years. SRJ is a prestige metric based on the idea that not all citations are the same. SJR uses a similar algorithm as the Google page rank; it provides a quantitative and qualitative measure of the journal's impact. SNIP measures contextual citation impact by wighting citations based on the total number of citations in a subject field. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease NAFLD is considered to be a manifestation of liver metabolic damage and is related to insulin resistance and genetic susceptibility. Additionally, the imbalance of certain pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines released by innate immunity is deemed to promote the steatosis of hepatocytes. In conclusion, this review indicates that the inflammatory and oxidative stress of KCs play a significant role in the development of NAFLD.. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease NAFLD , a type of metabolic liver damage that has affected Chinese citizens for years, is related to insulin resistance and genetic susceptibility. Meanwhile, NASH is histologically further defined as the emergence of inflammation and steatohepatitis with injury or fibrosis of hepatocytes. KCs are the resident macrophages in liver tissue that prevent harmful endotoxins present in the portal vein from entering into the circulation. Using chemicals to delete KCs has been demonstrated to alter the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and to alleviate hepatocellular damage. This topic is the centerpiece of this review.
Alveolar echinococcosis AEcaused by Echinococcus multilocularis. Cytokines secreted by activated KCs encourage differentiation of neighboring cells, such kupfer cells HSC to promote fibrogenesis, and recruit and activate other immune cells from bone marrow, which will further increase the anti-viral and inflammatory response.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Kupffer cells are a critical component of the mononuclear phagocytic system and are central to both the hepatic and systemic response to pathogens. Kupffer cells are reemerging as critical mediators of both liver injury and repair. Multiple M2 phenotypes can be distinguished, each involved in the resolution of inflammation and wound healing.
Kupffer Cells : Every day, living organisms like humans are subject to the attack of disease-causing agents called pathogens. Humans, for example, have various cells in the body which act to help deter the presence of pathogens. Check out the complete history of immunology and its timeline here. They are usually formed as a response to an infection or an accumulation of dead and damaged cells. Interestingly, macrophages in the body are modified to different structures and forms to adapt to various microorganisms and invaders. Also known as Kupffer-Browicz cells or stellate macrophages , these specialized macrophages are specifically found in the liver.
Kupfer cells
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October Learn More or Try it out now. Kupffer cells are a critical component of the mononuclear phagocytic system and are central to both the hepatic and systemic response to pathogens. Kupffer cells are reemerging as critical mediators of both liver injury and repair.
Swinglifestyle.com
Tissue-resident macrophages self-maintain locally throughout adult life with minimal contribution from circulating monocytes. Int Immunopharmacol. J Hepatol. Copy to clipboard. As detailed above, activation of Kupffer cells is an important contributor to hepatocyte injury in conditions of chronic inflammation. For experiments assessing resident immune cell phenotype, mice were euthanized, and then the lungs and liver were perfused with PBS through the portal vein, inferior vena cava, and the heart. Absence of individual transcription factors, such as early growth response-1 Egr-1 , controlling these responses to injury results in an impaired hepatoproliferative response and an increased susceptibility to hepatoxicity , , Prediction of risk of liver disease by alcohol intake, sex, and age: a prospective population study. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 23 , pp. J Inflammation, 7 , pp. The presence of a high level of LPS in the alcoholic liver activates KCs, and they release active mediators such as pro- inflammatory cytokines, eicosanoids and ROS. Some studies reported that classical M1 macrophages are anti-inflammatory, whereas alternative M2 macrophages are pro-inflammatory and pro-fibrogenic.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure.
Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: definition and pathology. The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author s and the copyright owner s are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. Michele T. This dual regulation of lipid metabolism and macrophage polarization is particularly interesting in light of the contributions of Kupffer cells and other hepatic macrophages to the progression of metabolic liver diseases, such as ALD and NASH, which are initially characterized by dysregulation in hepatic lipid metabolism see below. Therefore, timely administration of anti-fibrosis therapy is an important measure to hinder the progress of the disease. Annotations highlight genes associated with the cell cycle red , cell differentiation yellow , IFN blue and cell migration green. Based on the differential depletion effects of CEL on tumor-associated macrophages and KCs, we next specifically considered the role of KCs in the anti-metastatic activity of BG. Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative. In order to protect the stability of the liver microenvironment and repair the liver damage during the continuous stimulation of E. Liver-resident macrophage necroptosis orchestrates type 1 microbicidal inflammation and typemediated tissue repair during bacterial infection. Classical macrophages are IL- 12 high and IL low.

0 thoughts on “Kupfer cells”