Ph responsive polymers
In this review, we provide an analysis of some of the recent literature reports on the synthesis and ph responsive polymers of pH-responsive polymers. The review consists of various major parts including types of pH-responsive polymers, synthetic methods for their synthesis and their solution behaviors, their nanostructures in aqueous media, applications as LbL nanofilms, delivery devices, controlled release systems, sensors, stabilizers, solubilizers, ph responsive polymers, etc.
Kocak , C. Tuncer and V. E-mail: gkocak ogu. In this review, we provide an analysis of some of the recent literature reports on the synthesis and applications of pH-responsive polymers. The review consists of various major parts including types of pH-responsive polymers, synthetic methods for their synthesis and their solution behaviors, their nanostructures in aqueous media, applications as LbL nanofilms, delivery devices, controlled release systems, sensors, stabilizers, solubilizers, etc. In the last two decades, there have been great developments in synthetic methods and strategies for the preparation of novel pH-responsive polymers or polymeric materials providing possible materials for various applications including biotechnology, nanotechnology, colloid and surface science, materials science, etc. He is currently a PhD student in Prof.
Ph responsive polymers
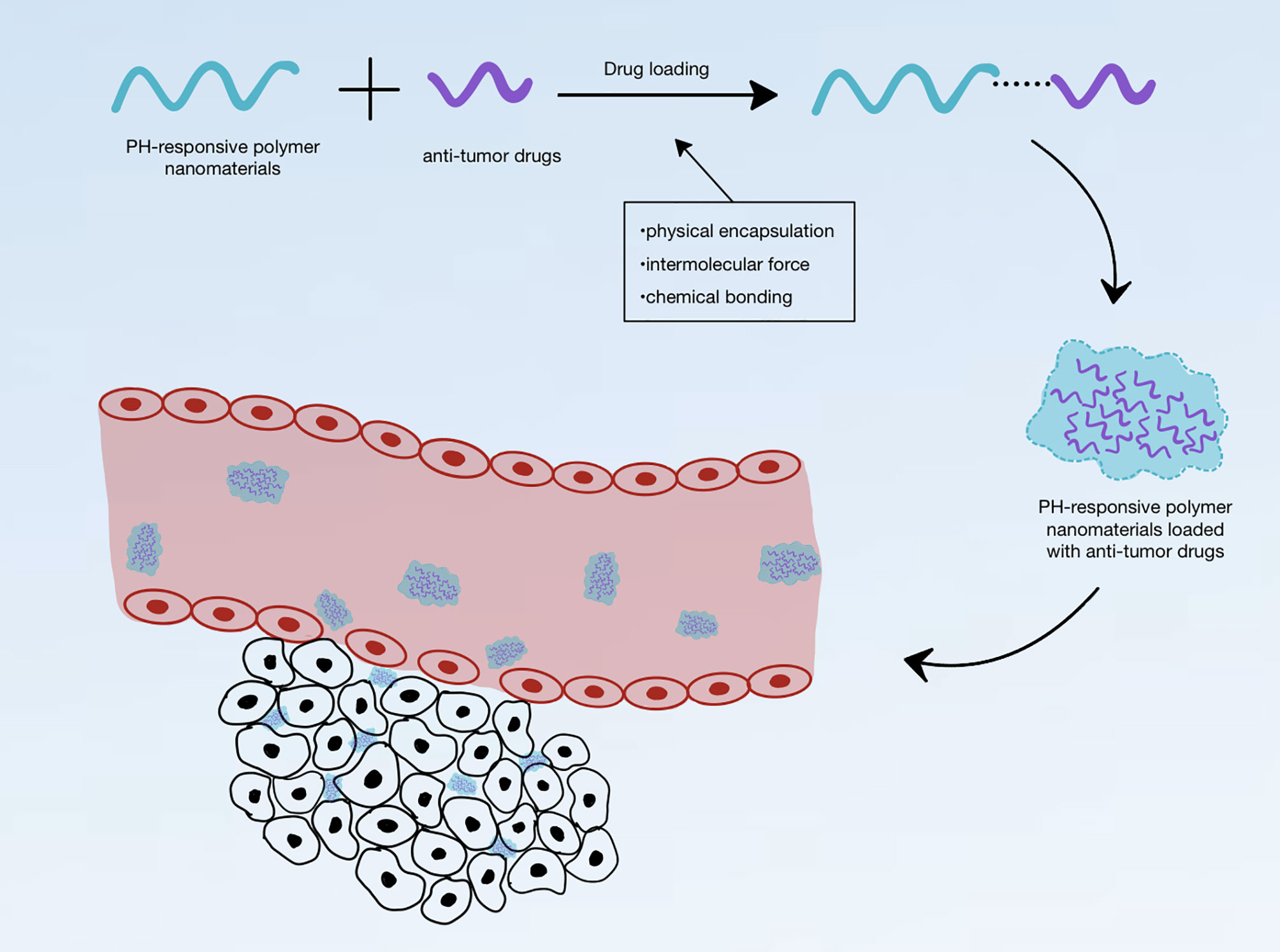
Materials may swell, collapse, or change depending on the pH of their environment. This behavior is exhibited due to the presence of certain functional groups in the polymer chain. These polymers can be designed with many different architectures for different applications. Key uses of pH sensitive polymers are controlled drug delivery systems, biomimetics , micromechanical systems, separation processes, and surface functionalization. The mechanism of response is the same for both, only the stimulus varies. The general form of the polymer is a backbone with functional "pendant groups" that hang off of it. Repulsions between like charges cause the polymers to change shape. Polyacids, also known as anionic polymers, are polymers that have acidic groups. Polyacids accept protons at low pH values. At higher pH values, they deprotonate and become negatively charged. This swelling behavior is observed when the pH is greater than the pKa of the polymer. Polybases are the basic equivalent of polyacids and are also known as cationic polymers. They accept protons at low pH like polyacids do, but they then become positively charged. In contrast, at higher pH values they are neutral.
Table 4 Types of micelles obtained from pH-responsive linear block copolymers.
.
In this review, we provide an analysis of some of the recent literature reports on the synthesis and applications of pH-responsive polymers. The review consists of various major parts including types of pH-responsive polymers, synthetic methods for their synthesis and their solution behaviors, their nanostructures in aqueous media, applications as LbL nanofilms, delivery devices, controlled release systems, sensors, stabilizers, solubilizers, etc. In the last two decades, there have been great developments in synthetic methods and strategies for the preparation of novel pH-responsive polymers or polymeric materials providing possible materials for various applications including biotechnology, nanotechnology, colloid and surface science, materials science, etc. Kocak, C. Tuncer and V. To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page. If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given.
Ph responsive polymers
Kocak , C. Tuncer and V. E-mail: gkocak ogu. In this review, we provide an analysis of some of the recent literature reports on the synthesis and applications of pH-responsive polymers. The review consists of various major parts including types of pH-responsive polymers, synthetic methods for their synthesis and their solution behaviors, their nanostructures in aqueous media, applications as LbL nanofilms, delivery devices, controlled release systems, sensors, stabilizers, solubilizers, etc. In the last two decades, there have been great developments in synthetic methods and strategies for the preparation of novel pH-responsive polymers or polymeric materials providing possible materials for various applications including biotechnology, nanotechnology, colloid and surface science, materials science, etc. He is currently a PhD student in Prof.
Joel and ellie porn
Dendrimer- graft -polymers. This article is part of the themed collection: Stimulus-responsive polymers. The DOX release profiles showed a pH dependent and slow release pattern. Polymers can be designed to respond to more than one external stimulus, such as pH and temperature. Jump to main content. Tools Tools. After its transfer to a lysosome, PDEA layer is further charged, disrupting the lysosomal membrane to release the nanoparticles into the cytosol. A pH change causes a change in the DNA compaction. These natural polymers have great importance among pH-responsive polymers. For example, polyacids release protons to become negatively charged at high pH. This self-assembly can occur due to the nature of the polymer and the solvent, or due to a change in pH. The copolymer has shown proton dissociation and dual ionic character. Search articles by author G. Please enable JavaScript to access the full features of the site or access our non-JavaScript page. In general, pH-responsive polymers of basic monomers behave as cationic polymers under acidic conditions and polymers with acidic monomers behave as anionic polymers under basic conditions.
Materials may swell, collapse, or change depending on the pH of their environment. This behavior is exhibited due to the presence of certain functional groups in the polymer chain.
The changes observed in polymers of different architectures by pH change are shown in Fig. These polymers undergo a phase transition above pH 5 owing to deprotonation of pyridine groups. Biodegradable microgel systems based on glycerol-1,3-diglycidyl ether cross-linked TEMPO-oxidized potato starch polymers are capable of absorbing a large amount of lysozyme. Tuncer a and V. Such groups are well known to be more hydrophilic in their anionic form. You have access to this article. Both Armes and Butun's groups have reported the synthesis of various PMEMA based polymers and investigation of their solution behaviors. DOX solubility is low at low pH values. The rate and extent of drug release can be controlled by varying the values of pH. Abstract In this review, we provide an analysis of some of the recent literature reports on the synthesis and applications of pH-responsive polymers. A novel pH-responsive nanogel with a pH-dependent charge conversion feature has also been developed for use as a possible anticancer drug delivery agent. The related polymer could form nanoparticles in aqueous solution and the particle size is dependent on solution pH. The pH-responsive polyacrylamide-modified hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose [ g -HPMC M ] graft copolymer has been synthesized via a microwave-assisted grafting method.

0 thoughts on “Ph responsive polymers”