Ploidy
Definition noun, plural: ploidies The number of sets of homologous chromosomes that make up the genome of a cell or an organism Supplement Ploidy refers to the number of sets of homologous chromosomes in the genome of a cell or an ploidy. Each set is designated by n, ploidy. Accordingly, one set of chromosome s, ploidy, 1nis described as monoploid.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Ploidy changes are frequent in nature and contribute to evolution, functional specialization and tumorigenesis. Analysis of model organisms of different ploidies revealed that increased ploidy leads to an increase in cell and nuclear volume, reduced proliferation, metabolic changes, lower fitness, and increased genomic instability, but the underlying mechanisms remain poorly understood. To investigate how gene expression changes with cellular ploidy, we analyzed isogenic series of budding yeasts from 1N to 4N.
Ploidy
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. The ability of an organism to replicate and segregate its genome with high fidelity is vital to its survival and for the production of future generations. Errors in either of these steps replication or segregation can lead to a change in ploidy or chromosome number. While these drastic genome changes can be detrimental to the organism, resulting in decreased fitness, they can also provide increased fitness during periods of stress. A change in ploidy or chromosome number can fundamentally change how a cell senses and responds to its environment. Here, we discuss current ideas within fungal biology that illuminate how eukaryotic genome size variation can impact the organism at a cellular and evolutionary level. One of the most fascinating observations from the last two decades of research is that some fungi have evolved the ability to tolerate large genome size changes and generate vast genomic heterogeneity without undergoing canonical meiosis. Cellular ploidy is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell. Many eukaryotic species have two diploid or more than two polyploid sets of chromosomes 1. These diploid and polyploid states are often the result of ancient whole genome duplication WGD or hybridization events that occurred throughout the evolution of plants, animals, and fungi 2 — 4. Ploidy changes also occur during the development of many organisms, and can vary within different tissues of the same organism and between individuals of the same species.
PLoS Biol, ploidy. Ploidy changes and genome stability in yeast. Oberpriller; A Mauro
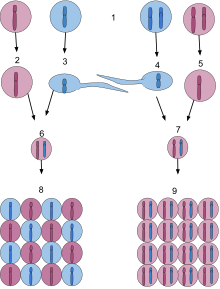
Sets of chromosomes refer to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, respectively, in each homologous chromosome pair, which chromosomes naturally exist as. Somatic cells , tissues , and individual organisms can be described according to the number of sets of chromosomes present the "ploidy level" : monoploid 1 set , diploid 2 sets , triploid 3 sets , tetraploid 4 sets , pentaploid 5 sets , hexaploid 6 sets , heptaploid [2] or septaploid [3] 7 sets , etc. The generic term polyploid is often used to describe cells with three or more sets of chromosomes. Virtually all sexually reproducing organisms are made up of somatic cells that are diploid or greater, but ploidy level may vary widely between different organisms, between different tissues within the same organism, and at different stages in an organism's life cycle. Half of all known plant genera contain polyploid species, and about two-thirds of all grasses are polyploid. In some species, ploidy varies between individuals of the same species as in the social insects , and in others entire tissues and organ systems may be polyploid despite the rest of the body being diploid as in the mammalian liver.
Genome Biology volume 25 , Article number: 62 Cite this article. Metrics details. Cancer cells often exhibit DNA copy number aberrations and can vary widely in their ploidy. Correct estimation of the ploidy of single-cell genomes is paramount for downstream analysis. Based only on single-cell DNA sequencing information, scAbsolute achieves accurate and unbiased measurement of single-cell ploidy and replication status, including whole-genome duplications. Many common cancers are characterised by chromosomal instability CIN and, as a result, extensive copy number aberrations CNAs [ 1 , 2 ]. CNAs alter the number of copies of genomic regions in a cell, thus creating a background of genomic variation on which selection can act [ 3 ]. CNAs can act as drivers of cancer evolution [ 4 , 5 , 6 ] and be used to infer phylogenies [ 7 , 8 , 9 ]. Importantly, CNAs have been shown to play a crucial role in cancer treatment and prognosis [ 10 , 11 , 12 ], and they correlate with markers of immune evasion and increased activity in proliferation pathways [ 6 , 13 , 14 ]. As a consequence of CIN, tumour cells, unlike most normal cells, substantially vary in the amount of DNA they contain, the so-called ploidy.
Ploidy
Cell division cycle, figure from Wikipedia. Cells that stop dividing exit the G1 phase of the cell cycle into a so-called G0 state. Cells reproduce genetically identical copies of themselves by cycles of cell growth and division. The cell cycle diagram on the left shows that a cell division cycle consists of 4 stages:. Chromosomes were first named by cytologists viewing dividing cells through a microscope.
Bitmojis
From FastQ data to high confidence variant calls: the genome analysis toolkit best practices pipeline. Cell and tissue culture can be used to maintain genotypes or to obtain novel genotypes. Aneuploid chromosomes are highly unstable during DNA transformation of Candida albicans. BMC Genomics. Letters are often used to indicate to the different source species that have been identified as contributors to crop genomes. Banana Musa spp. Specific terms are triploid 3 sets , tetraploid 4 sets , pentaploid 5 sets , hexaploid 6 sets , heptaploid [2] or septaploid [3] 7 sets , octoploid 8 sets , nonaploid 9 sets , decaploid 10 sets , undecaploid 11 sets , dodecaploid 12 sets , tridecaploid 13 sets , tetradecaploid 14 sets , etc. Dramatic ploidy changes have been observed during infection. Additional file 1 Supplementary figures addressing the effect of denoising, as well as the effect of high coverage outliers on the likelihood of Gaussian and binomial mixtures. The diploidized cells have significantly higher fitness than the isogenic progenitor strains in competition experiments Source data are provided in Supplementary Tables and as a Source Data file. EMBO J. PCR products were transformed into a haploid strain, or into diploid strains and the heterozygous diploids were sporulated and dissected to select for haploids with drug resistance. In addition to mutations in RAD52 , null mutations in CTF18 involved in sister chromatid cohesion also lead to rapid genome reduction from diploidy to haploidy For example, a mutation may cause aneuploidy, which then gives rise to a whole genome ploidy change.
Aleeza C. Gerstein, Sarah P.
Polyploidy and genome restructuring: a variety of outcomes. Pan-cancer patterns of somatic copy number alteration. Experimental evolution reveals interplay between Sch9 and polyploid stability in yeast. Breeders and geneticists use aneuploids as a tool to identify the chromosomal location of specific genes, or substitute a particular chromosome into a genotype. Bibcode : PNAS.. Haploid plants are very valuable in certain breeding applications. A tetraploid intermediate precedes aneuploid formation in yeasts exposed to fluconazole. Galitski, T. Ploidy variation in multinucleate cells changes under stress. The Beneficial Effects of Ploidy Changes Adaptation of an organism to a novel environment is a function of the rate in which beneficial, growth-promoting mutations are acquired and spread throughout the population. Mol Plant Pathol. Aneuploidy, in particular the amplification of chromosome 1, has also been observed in response to antifungal drug stress 42 , J Med Genet. Virtually all sexually reproducing organisms are made up of somatic cells that are diploid or greater, but ploidy level may vary widely between different organisms, between different tissues within the same organism, and at different stages in an organism's life cycle. In a process known as diploidization over time polyploid genomes may return to diploid status, although certain genes may be retained in multiple copies.

Rather useful idea
To think only!
Bravo, what words..., a magnificent idea