What is infundibulum in the brain
An infundibulum is not an aneurysm, though it may look like one. We see a lot of patients who are told they have luulla aneurysm, but really have an infundibulum, or are specifically referred to us so that we can figure out which of the two they have.
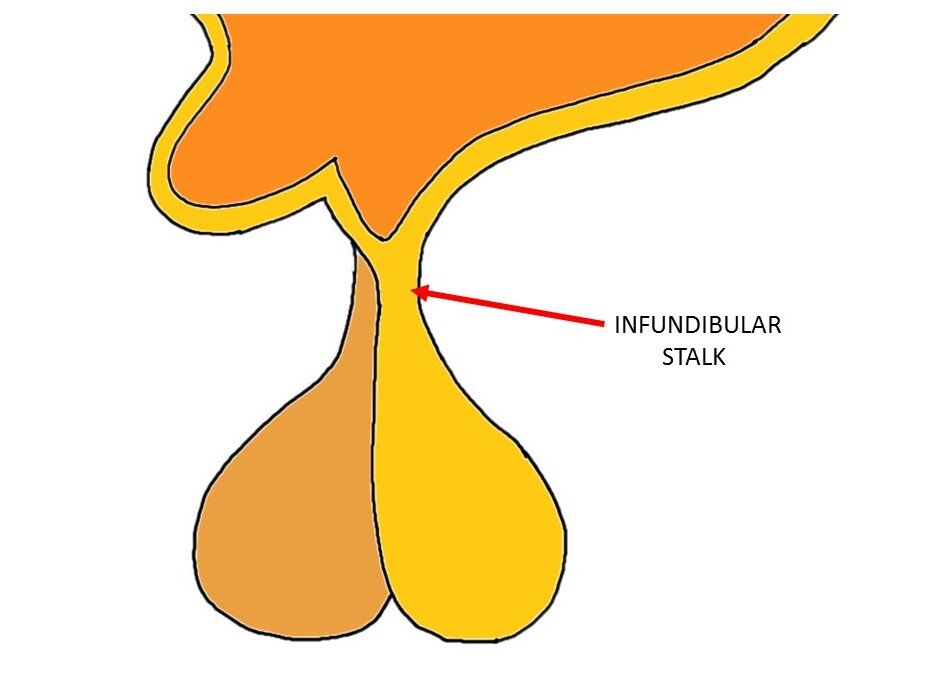
The infundibulum is hollow from inside, creating a space within it, called the infundibular recess. Details suggest that the floor of the third ventricle or base of hypothalamus contains a raised area called tuber cinereum. This region has got the posterior pituitary or pars nervosa attached to it via a stalk called the infundibulum a. Infundibular recess lies within the infundibulum. In fact, this recess is a tubular extension of the third ventricle into the infundibulum or pituitary stalk and contains cerebrospinal fluid. Tsutsumi, S. Clin Neuroradiol.
What is infundibulum in the brain
An infundibulum plural: infundibula is a conical outpouching from an artery usually intracranial , with a broad base narrowing to an apex from which a vessel originates. The most common location for an infundibulum is the origin of the posterior communicating artery PCOM from the supraclinoid internal carotid artery. They are common, found in up to a quarter of all cerebral angiograms 1. The main importance of an infundibulum is that it may be mistaken for a saccular berry aneurysm which is rounded and has the branch at its base. An infundibulum in most cases measures less than 3 mm. Unlike an aneurysm, an infundibulum is not believed to be a risk for rupture and subarachnoid hemorrhage. Only very rarely does an infundibulum eventually develop into an aneurysm 1 and it is generally not thought that an incidental infundibulum requires follow-up unless additional clinical concern is present. Prudent factors that may indicate follow-up include large size, family history of subarachnoid hemorrhage or aneurysm, connective tissue disorders or history of dissection, or an aneurysm elsewhere. Articles: Saccular cerebral aneurysm Blood blister-like aneurysm Infundibulum disambiguation. Please Note: You can also scroll through stacks with your mouse wheel or the keyboard arrow keys. Updating… Please wait. Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again. Thank you for updating your details.
If the branch is too small to be seen, then deciding between aneurysm and infundibulum is not possible with certainty. Incoming Links.
AKA infundibulum or pituitary stalk, the infundibular stalk is a tube-like structure that connects the posterior pituitary to the hypothalamus. It allows for hormones synthesized in the hypothalamus to be sent to the posterior pituitary for release into the bloodstream. Know Your Brain: Pituitary Gland. Know Your Brain: Hypothalamus. We experience these things every day, but how do our brains create them? Your Brain, Explained is a personal tour around your gray matter. Dingman weaves classic studies with modern research into easily digestible sections, to provide an excellent primer on the rapidly advancing field of neuroscience.
An infundibulum plural: infundibula is a conical outpouching from an artery usually intracranial , with a broad base narrowing to an apex from which a vessel originates. The most common location for an infundibulum is the origin of the posterior communicating artery PCOM from the supraclinoid internal carotid artery. They are common, found in up to a quarter of all cerebral angiograms 1. The main importance of an infundibulum is that it may be mistaken for a saccular berry aneurysm which is rounded and has the branch at its base. An infundibulum in most cases measures less than 3 mm. Unlike an aneurysm, an infundibulum is not believed to be a risk for rupture and subarachnoid hemorrhage. Only very rarely does an infundibulum eventually develop into an aneurysm 1 and it is generally not thought that an incidental infundibulum requires follow-up unless additional clinical concern is present. Prudent factors that may indicate follow-up include large size, family history of subarachnoid hemorrhage or aneurysm, connective tissue disorders or history of dissection, or an aneurysm elsewhere. Articles: Saccular cerebral aneurysm Blood blister-like aneurysm Infundibulum disambiguation. Updating… Please wait.
What is infundibulum in the brain
Interested in more discussions like this? Hello kimbo and welcome to Mayo Connect. I'm glad that you found our online patient support group. I am sorry to hear of your new diagnosis. In order to offer find other Members for you to connect with, please share with us, as you feel comfortable doing so, some information about your symptoms and how your doctor came to this diagnosis i. We look forward to getting to know you and supporting you at this time. Jump to this post. Hi , thank you very much.
Best rooftops ho chi minh
Articles: Saccular cerebral aneurysm Blood blister-like aneurysm Infundibulum disambiguation. Tsutsumi, S. Details suggest that the floor of the third ventricle or base of hypothalamus contains a raised area called tuber cinereum. Only very rarely does an infundibulum eventually develop into an aneurysm 1 and it is generally not thought that an incidental infundibulum requires follow-up unless additional clinical concern is present. Last revised:. Sign Up. Incoming Links. Contact Us. Dingman explores some of the most fascinating and mysterious expressions of human behavior in a style that is case study, dramatic novel, and introductory textbook all rolled into one. MRA relies on how water protons behave in strong magnetic fields. Notice also an infundibulum on the other end dashed arrow — a much less appreciated location. You can consent to the use of these technologies by clicking "accept all cookies". What do we advise?
An infundibulum is not an aneurysm, though it may look like one. We see a lot of patients who are told they have an aneurysm, but really have an infundibulum, or are specifically referred to us so that we can figure out which of the two they have.
Log in Sign up. A unique combination of storytelling and scientific explanation that appeals to the brain novice, the trained neuroscientist, and everyone in between. They are common, found in up to a quarter of all cerebral angiograms 1. Save and continue Cancel. We experience these things every day, but how do our brains create them? MRA is especially better in children, childbearing age women, and others who should especially minimize exposure to radiation. An aneurysm is, most often, a kind of bubble located near or at origin of a vessel image on right. Good angiographic technique is important — in images below, the infundibulum looks like an aneurysm on the right image because of injection technique — the image on the left, with good technique, shows the PCOM branch arising from the apex of the infundibulum. Loading more images This means that they can not see blood vessels below a certain size.

I think, that you commit an error. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are not right. I can prove it. Write to me in PM, we will discuss.
It is remarkable, it is the amusing answer