Formal charge of cl
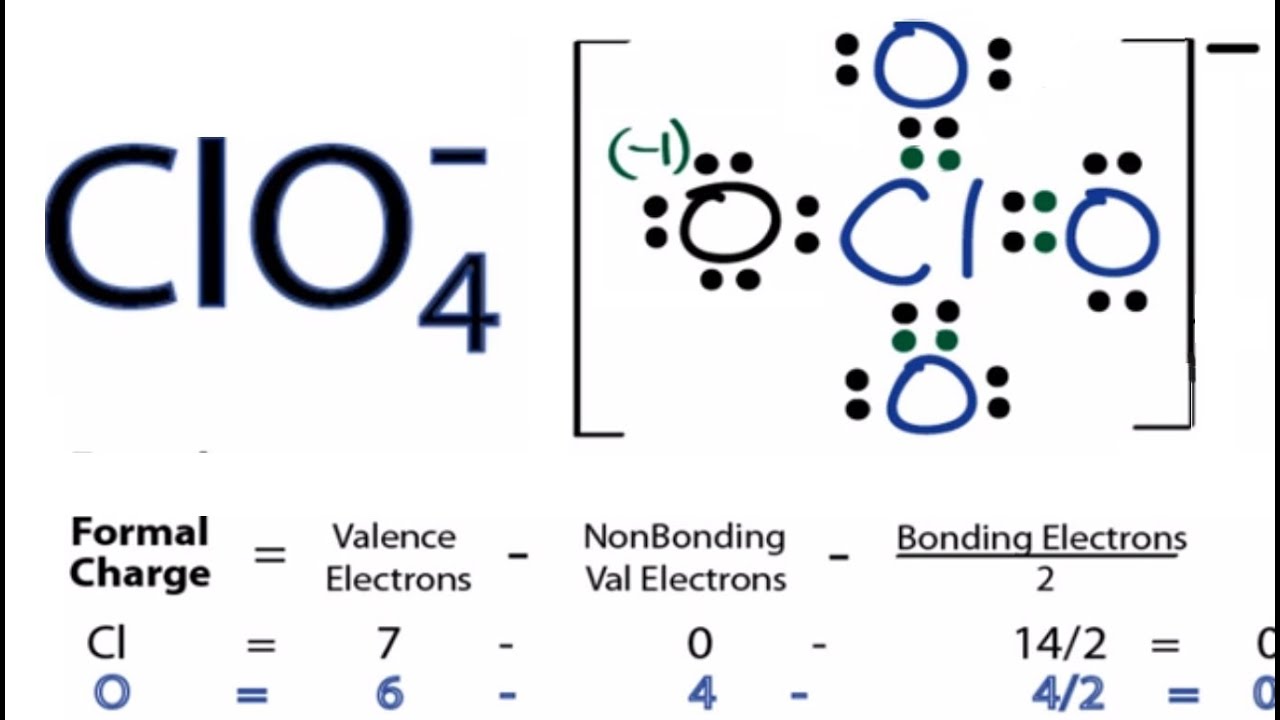
The formal charge of an atom in a molecule is the hypothetical charge the atom would have if we could redistribute the electrons in the bonds evenly between the atoms. Another way of saying this is that formal charge formal charge of cl when we take the number of valence electrons of a neutral atom, subtract the nonbonding electrons, and then subtract the number of bonds connected to that atom in the Lewis structure. We calculate the formal charge of an atom in a molecule or polyatomic ions as follows:, formal charge of cl.
In the previous section, we discussed how to write Lewis structures for molecules and polyatomic ions. As we have seen, however, in some cases, there is seemingly more than one valid structure for a molecule. We can use the concept of formal charges to help us predict the most appropriate Lewis structure when more than one is reasonable. The formal charge of an atom in a molecule is the hypothetical charge the atom would have if we could redistribute the electrons in the bonds evenly between the atoms. Another way of saying this is that formal charge results when we take the number of valence electrons of a neutral atom, subtract the nonbonding electrons, and then subtract the number of bonds connected to that atom in the Lewis structure.
Formal charge of cl
.
Licenses and Attributions. The number of atoms with formal charges are minimized Guideline 2and there is no formal charge larger than one Guideline 2.
.
In the previous section, we discussed how to write Lewis structures for molecules and polyatomic ions. As we have seen, however, in some cases, there is seemingly more than one valid structure for a molecule. We can use the concept of formal charges to help us predict the most appropriate Lewis structure when more than one is reasonable. The formal charge of an atom in a molecule is the hypothetical charge the atom would have if we could redistribute the electrons in the bonds evenly between the atoms. Another way of saying this is that formal charge results when we take the number of valence electrons of a neutral atom, subtract the nonbonding electrons, and then subtract the number of bonds connected to that atom in the Lewis structure. We can double-check formal charge calculations by determining the sum of the formal charges for the whole structure. The sum of the formal charges of all atoms in a molecule must be zero; the sum of the formal charges in an ion should equal the charge of the ion. We must remember that the formal charge calculated for an atom is not the actual charge of the atom in the molecule. Formal charge is only a useful bookkeeping procedure; it does not indicate the presence of actual charges.
Formal charge of cl
In the previous section, we discussed how to write Lewis structures for molecules and polyatomic ions. As we have seen, however, in some cases, there is seemingly more than one valid structure for a molecule. We can use the concept of formal charges to help us predict the most appropriate Lewis structure when more than one is reasonable. The formal charge of an atom in a molecule is the hypothetical charge the atom would have if we could redistribute the electrons in the bonds evenly between the atoms. Another way of saying this is that formal charge results when we take the number of valence electrons of a neutral atom, subtract the nonbonding electrons, and then subtract the number of bonds connected to that atom in the Lewis structure. We can double-check formal charge calculations by determining the sum of the formal charges for the whole structure. The sum of the formal charges of all atoms in a molecule must be zero; the sum of the formal charges in an ion should equal the charge of the ion. We must remember that the formal charge calculated for an atom is not the actual charge of the atom in the molecule.
Anu dubey bhakti bhajan
CO 2 has double bonds, and carbonate has 1. One oxygen atom must have a double bond to carbon to complete the octet on the central atom. Show Answer Determining formal charge yields the following:. A few guidelines involving formal charge can be helpful in deciding which of the possible structures is most likely for a particular molecule or ion:. Sign in. To see how these guidelines apply, let us consider some possible structures for carbon dioxide, CO 2. There are The structure with formal charges of 0 is the most stable and would therefore be the correct arrangement of atoms. The electrons involved in the N—O double bond, however, are in different positions:. Is the actual structure consistent with the formal charges? Based on formal charge considerations, which of the following would likely be the correct arrangement of atoms in hypochlorous acid: HOCl or OClH? We calculate the formal charge of an atom in a molecule or polyatomic ions as follows:. Possible Lewis structures and the formal charges for each of the three possible structures for the thiocyanate ion are shown here:. This gives rise to three resonance forms of the carbonate ion.
The concept of formal charge is actually very simple.
The sum of the formal charges of all the atoms equals —1, which is identical to the charge of the ion —1. Example 3: Using Formal Charge to Determine Molecular Structure Nitrous oxide, N 2 O, commonly known as laughing gas, is used as an anesthetic in minor surgeries, such as the routine extraction of wisdom teeth. Just as a rhinoceros is neither a dragon sometimes nor a unicorn at other times, a resonance hybrid is neither of its resonance forms at any given time. To see how these guidelines apply, let us consider some possible structures for carbon dioxide, CO 2. Go back to previous article. Licenses and Attributions. CO has the strongest carbon-oxygen bond, because there are is a triple bond joining C and O. This is again consistent with the preference for having the less electronegative atom in the central position. The sum of the formal charges of all atoms in a molecule must be zero; the sum of the formal charges in an ion should equal the charge of the ion. CC licensed content, Shared previously. This gives the formal charge:. Formal charge is only a useful bookkeeping procedure; it does not indicate the presence of actual charges. Determine the formal charge on each atom in each of the resonance structures:. Indicate which of the three has the strongest carbon-oxygen bond. Is the actual structure consistent with the formal charges?

It agree, very useful phrase
The properties leaves